Effects of Agricultural Management of Spent Mushroom Waste on Phytotoxicity and Microbiological Transformations of C, P, and S in Soil and Their Consequences for the Greenhouse Effect
- PMID: 36232214
- PMCID: PMC9565085
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph191912915
Effects of Agricultural Management of Spent Mushroom Waste on Phytotoxicity and Microbiological Transformations of C, P, and S in Soil and Their Consequences for the Greenhouse Effect
Abstract
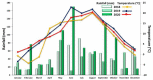
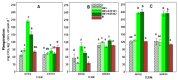
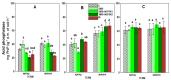
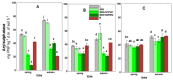
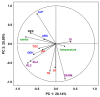
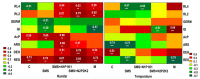
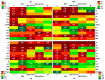
The huge volumes of currently generated agricultural waste pose a challenge to the economy of the 21st century. One of the directions for their reuse may be as fertilizer. Spent mushroom substrate (SMS) could become an alternative to manure (M). A three-year field experiment was carried out, in which the purpose was to test and compare the effect of SMS alone, as well as in multiple variants with mineral fertilization, and in manure with a variety of soil quality indices-such as enzymatic activity, soil phytotoxicity, and greenhouse gas emissions, i.e., CO2. The use of SMS resulted in significant stimulation of respiratory and dehydrogenase activity. Inhibition of acid phosphatase and arylsulfatase activity via SMS was recorded. SMS showed varying effects on soil phytotoxicity, dependent on time. A positive effect was noted for the growth index (GI), while inhibition of root growth was observed in the first two years of the experiment. The effect of M on soil respiratory and dehydrogenase activity was significantly weaker compared to SMS. Therefore, M is a safer fertilizer as it does not cause a significant persistent increase in CO2 emissions. Changes in the phytotoxicity parameters of the soil fertilized with manure, however, showed a similar trend as in the soil fertilized with SMS.
Keywords: Lepidium sativum L.; dehydrogenases; enzymatic activity; greenhouse effect; manure; phytotoxicity; soil microorganisms; soil respiration; spent mushroom substrate; waste.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Effects of spent mushroom substrate-derived biochar on soil CO2 and N2O emissions depend on pyrolysis temperature.Chemosphere. 2020 May;246:125608. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125608. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Chemosphere. 2020. PMID: 31884231
-
[Effects of Mushroom Residue Application Rates on Net Greenhouse Gas Emissions in the Purple Paddy Soil].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2018 Jun 8;39(6):2827-2836. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201711029. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2018. PMID: 29965641 Chinese.
-
Effects of calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer, biochar and spent mushroom substrate on compost maturity and gaseous emissions during pig manure composting.J Environ Manage. 2020 Aug 1;267:110649. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110649. Epub 2020 Apr 29. J Environ Manage. 2020. PMID: 32364133
-
Unlocking the Potential of Spent Mushroom Substrate (SMS) for Enhanced Agricultural Sustainability: From Environmental Benefits to Poultry Nutrition.Life (Basel). 2023 Sep 22;13(10):1948. doi: 10.3390/life13101948. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Greenhouse gas emissions from inorganic and organic fertilizer production and use: A review of emission factors and their variability.J Environ Manage. 2020 Dec 15;276:111211. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111211. Epub 2020 Sep 25. J Environ Manage. 2020. PMID: 32987233 Review.
Cited by
-
Plant-Derived Waste as a Component of Growing Media: Manifestations, Assessments, and Sources of Their Phytotoxicity.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jul 22;13(14):2000. doi: 10.3390/plants13142000. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spent Mushroom Substrate Improves Microbial Quantities and Enzymatic Activity in Soils of Different Farming Systems.Microorganisms. 2024 Jul 24;12(8):1521. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081521. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203364 Free PMC article.
-
Spent Mushroom Substrate-Derived Biochar and Its Applications in Modern Agricultural Systems: An Extensive Overview.Life (Basel). 2025 Feb 18;15(2):317. doi: 10.3390/life15020317. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40003725 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adejumo I.O., Adebiyi O.A. Agricultural solid wastes: Causes, effects, and effective management. In: Saleh H.M., editor. Strategies of Sustainable Solid Waste Management. Intech Open; London, UK: 2020. - DOI
-
- Hanafi M.F.H., Rezania S., Taib M.S., Md Din M.F., Yamauchi M., Sakamoto M., Hara H., Park J., Ebrahimi S.S. Environmentally sustainable applications of agro-based spent mushroom substrate (SMS): An overview. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018;20:1383–1396. doi: 10.1007/s10163-018-0739-0. - DOI
-
- FAOSTAT Crops and Livestock Products. 2022. [(accessed on 28 July 2022)]. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#rankings/countries_by_commodity.
-
- Cunha Zied D., Sánchez J.E., Noble R., Pardo-Giménez A. Use of spent mushroom substrate in new mushroom crops to promote the transition towards a circular economy. Agronomy. 2020;10:1239. doi: 10.3390/agronomy10091239. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

