Role of Endothelin-1 in Right Atrial Arrhythmogenesis in Rabbits with Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- PMID: 36232308
- PMCID: PMC9569916
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231910993
Role of Endothelin-1 in Right Atrial Arrhythmogenesis in Rabbits with Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
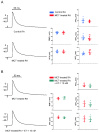
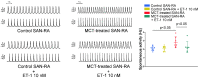
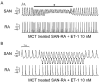
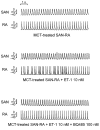
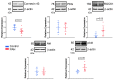
Atrial arrhythmias are considered prominent phenomena in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) resulting from atrial electrical and structural remodeling. Endothelin (ET)-1 levels correlate with PAH severity and are associated with atrial remodeling and arrhythmia. In this study, hemodynamic measurement, western blot analysis, and histopathology were performed in the control and monocrotaline (MCT, 60 mg/kg)-induced PAH rabbits. Conventional microelectrodes were used to simultaneously record the electrical activity in the isolated sinoatrial node (SAN) and right atrium (RA) tissue preparations before and after ET-1 (10 nM) or BQ-485 (an ET-A receptor antagonist, 100 nM) perfusion. MCT-treated rabbits showed an increased relative wall thickness in the pulmonary arterioles, mean cell width, cross-sectional area of RV myocytes, and higher right ventricular systolic pressure, which were deemed to have PAH. Compared to the control, the spontaneous beating rate of SAN-RA preparations was faster in the MCT-induced PAH group, which can be slowed down by ET-1. MCT-induced PAH rabbits had a higher incidence of sinoatrial conduction blocks, and ET-1 can induce atrial premature beats or short runs of intra-atrial reentrant tachycardia. BQ 485 administration can mitigate ET-1-induced RA arrhythmogenesis in MCT-induced PAH. The RA specimens from MCT-induced PAH rabbits had a smaller connexin 43 and larger ROCK1 and phosphorylated Akt than the control, and similar PKG and Akt to the control. In conclusion, ET-1 acts as a trigger factor to interact with the arrhythmogenic substrate to initiate and maintain atrial arrhythmias in PAH. ET-1/ET-A receptor/ROCK signaling may be a target for therapeutic interventions to treat PAH-induced atrial arrhythmias.
Keywords: Endothelin-1; atrial arrhythmogenesis; pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors hereby declare to have no conflict of interest regarding this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pinocembrin attenuates susceptibility to atrial fibrillation in rats with pulmonary arterial hypertension.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 5;960:176169. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176169. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37925134
-
Development of occlusive neointimal lesions in distal pulmonary arteries of endothelin B receptor-deficient rats: a new model of severe pulmonary arterial hypertension.Circulation. 2005 Jun 7;111(22):2988-96. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.491456. Epub 2005 May 31. Circulation. 2005. PMID: 15927975 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of Dapagliflozin on the vulnerability of ventricular arrhythmia in rats with pulmonary artery hypertension induced by monocrotaline.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):2697-2709. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2017652. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35042435 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin43, A Promising Target to Reduce Cardiac Arrhythmia Burden in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 14;25(6):3275. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063275. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arrhythmic Burden and Outcomes in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Front Med (Lausanne). 2019 Jul 23;6:169. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00169. eCollection 2019. Front Med (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31396515 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isolated Left Atrium Morphofunctional Study of an Experimental Pulmonary Hypertension Model in Rats.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2023 Sep;120(10):e20230188. doi: 10.36660/abc.20230188. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37878960 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese.
-
Revisiting Virchow's triad: exploring the cellular and molecular alterations in cerebral venous congestion.Cell Biosci. 2024 Oct 23;14(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01314-5. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39444013 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Signaling Regulation of Sinoatrial Node Dysfunction.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2023 Jul;25(7):621-630. doi: 10.1007/s11886-023-01885-8. Epub 2023 May 25. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37227579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypertension Induces Pro-arrhythmic Cardiac Connexome Disorders: Protective Effects of Treatment.Biomolecules. 2023 Feb 9;13(2):330. doi: 10.3390/biom13020330. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36830700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of pulmonary arterial hypertension-induced atrial fibrillation: insights from multi-scale models of the human atria.Interface Focus. 2023 Dec 15;13(6):20230039. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2023.0039. eCollection 2023 Dec 6. Interface Focus. 2023. PMID: 38106916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng C.P., Ukai T., Onishi K., Ohte N., Suzuki M., Zhang Z.S., Cheng H.J., Tachibana H., Igawa A., Little W.C. The role of ANG II and endothelin-1 in exercise-induced diastolic dysfunction in heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001;280:H1853–H1860. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.2001.280.4.H1853. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MOST108-2314-B-281-007-MY3, MOST109-2314-B-038-124-MY3, MOST110-2314-B-038-129, MOST110-2314-B-038-107-MY3, and MOST110-2314-B-016-037-MY3/the Ministry of Science and Technology
- MND-MAB-D-11209/Ministry of National Defense-Medical Affairs Bureau
- 2-02-005/the Foundation for the Development of Internal Medicine in Okinawa
- CGH-MR-A11109/Cathay General Hospital
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

