Role of Endothelin-1 in Right Atrial Arrhythmogenesis in Rabbits with Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- PMID: 36232308
- PMCID: PMC9569916
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231910993
Role of Endothelin-1 in Right Atrial Arrhythmogenesis in Rabbits with Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
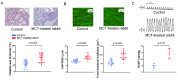
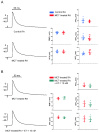
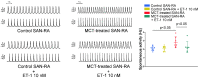
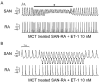
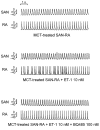
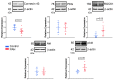
Atrial arrhythmias are considered prominent phenomena in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) resulting from atrial electrical and structural remodeling. Endothelin (ET)-1 levels correlate with PAH severity and are associated with atrial remodeling and arrhythmia. In this study, hemodynamic measurement, western blot analysis, and histopathology were performed in the control and monocrotaline (MCT, 60 mg/kg)-induced PAH rabbits. Conventional microelectrodes were used to simultaneously record the electrical activity in the isolated sinoatrial node (SAN) and right atrium (RA) tissue preparations before and after ET-1 (10 nM) or BQ-485 (an ET-A receptor antagonist, 100 nM) perfusion. MCT-treated rabbits showed an increased relative wall thickness in the pulmonary arterioles, mean cell width, cross-sectional area of RV myocytes, and higher right ventricular systolic pressure, which were deemed to have PAH. Compared to the control, the spontaneous beating rate of SAN-RA preparations was faster in the MCT-induced PAH group, which can be slowed down by ET-1. MCT-induced PAH rabbits had a higher incidence of sinoatrial conduction blocks, and ET-1 can induce atrial premature beats or short runs of intra-atrial reentrant tachycardia. BQ 485 administration can mitigate ET-1-induced RA arrhythmogenesis in MCT-induced PAH. The RA specimens from MCT-induced PAH rabbits had a smaller connexin 43 and larger ROCK1 and phosphorylated Akt than the control, and similar PKG and Akt to the control. In conclusion, ET-1 acts as a trigger factor to interact with the arrhythmogenic substrate to initiate and maintain atrial arrhythmias in PAH. ET-1/ET-A receptor/ROCK signaling may be a target for therapeutic interventions to treat PAH-induced atrial arrhythmias.
Keywords: Endothelin-1; atrial arrhythmogenesis; pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors hereby declare to have no conflict of interest regarding this article.
Figures

References
-
- Cheng C.P., Ukai T., Onishi K., Ohte N., Suzuki M., Zhang Z.S., Cheng H.J., Tachibana H., Igawa A., Little W.C. The role of ANG II and endothelin-1 in exercise-induced diastolic dysfunction in heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001;280:H1853–H1860. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.2001.280.4.H1853. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MOST108-2314-B-281-007-MY3, MOST109-2314-B-038-124-MY3, MOST110-2314-B-038-129, MOST110-2314-B-038-107-MY3, and MOST110-2314-B-016-037-MY3/the Ministry of Science and Technology
- MND-MAB-D-11209/Ministry of National Defense-Medical Affairs Bureau
- 2-02-005/the Foundation for the Development of Internal Medicine in Okinawa
- CGH-MR-A11109/Cathay General Hospital
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

