Rhamnolipid Micellization and Adsorption Properties
- PMID: 36232408
- PMCID: PMC9570487
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231911090
Rhamnolipid Micellization and Adsorption Properties
Abstract
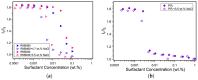
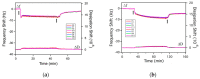
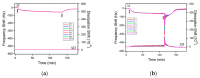
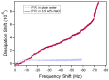
Biosurfactants are naturally occurring amphiphiles that are being actively pursued as alternatives to synthetic surfactants in cleaning, personal care, and cosmetic products. On the basis of their ability to mobilize and disperse hydrocarbons, biosurfactants are also involved in the bioremediation of oil spills. Rhamnolipids are low molecular weight glycolipid biosurfactants that consist of a mono- or di-rhamnose head group and a hydrocarbon fatty acid chain. We examine here the micellization of purified mono-rhamnolipids and di-rhamnolipids in aqueous solutions and their adsorption on model solid surfaces. Rhamnolipid micellization in water is endothermic; the CMC (critical micellization concentration) of di-rhamnolipid is lower than that of mono-rhamnolipid, and both CMCs decrease upon NaCl addition. Rhamnolipid adsorption on gold surface is mostly reversible and the adsorbed layer is rigid. A better understanding of biosurfactant self-assembly and adsorption properties is important for their utilization in consumer products and environmental applications.
Keywords: bioremediation; biosurfactant; formulation; green surfactant; rhamnolipid; self-assembly; sustainability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Vieira I.M.M., Santos B.L.P., Ruzene D.S., Silva D.P. An overview of current research and developments in biosurfactants. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021;100:1–18. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2021.05.017. - DOI
-
- Souza E.C., Vessoni-Penna T.C., de Souza Oliveira R.P. Biosurfactant-enhanced hydrocarbon bioremediation: An overview. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014;89:88–94. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.01.007. - DOI
-
- Chronakis I.S., Alexandridis P. Rheological properties of oppositely charged polyelectrolyte−surfactant mixtures: Effect of polymer molecular weight and surfactant architecture. Macromolecules. 2001;34:5005–5018. doi: 10.1021/ma000609k. - DOI
-
- Kancharla S., Bedrov D., Tsianou M., Alexandridis P. Structure and composition of mixed micelles formed by nonionic block copolymers and ionic surfactants in water determined by small-angle neutron scattering with contrast variation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;609:456–468. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.10.176. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

