Characterization of New Defensin Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Expression in Bed Bugs in Response to Bacterial Ingestion and Injection
- PMID: 36232802
- PMCID: PMC9570333
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231911505
Characterization of New Defensin Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Expression in Bed Bugs in Response to Bacterial Ingestion and Injection
Abstract
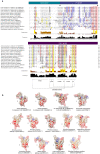
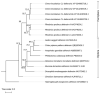
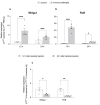
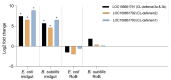
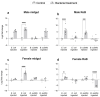
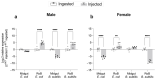
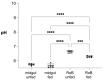
Common bed bugs, Cimex lectularius, can carry, but do not transmit, pathogens to the vertebrate hosts on which they feed. Some components of the innate immune system of bed bugs, such as antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), eliminate the pathogens. Here, we determined the molecular characteristics, structural properties, and phylogenetic relatedness of two new defensins (CL-defensin1 (XP_024085718.1), CL-defensin2 (XP_014240919.1)), and two new defensin isoforms (CL-defensin3a (XP_014240918.1), CL-defensin3b (XP_024083729.1)). The complete amino acid sequences of CL-defensin1, CL-defensin2, CL-defensin3a, and CL-defensin3b are strongly conserved, with only minor differences in their signal and pro-peptide regions. We used a combination of comparative transcriptomics and real-time quantitative PCR to evaluate the expression of these defensins in the midguts and the rest of the body of insects that had been injected with bacteria or had ingested blood containing the Gram-positive (Gr+) bacterium Bacillus subtilis and the Gram-negative (Gr-) bacterium Escherichia coli. We demonstrate, for the first time, sex-specific and immunization mode-specific upregulation of bed bug defensins in response to injection or ingestion of Gr+ or Gr- bacteria. Understanding the components, such as these defensins, of the bed bugs' innate immune systems in response to pathogens may help unravel why bed bugs do not transmit pathogens to vertebrates.
Keywords: Toll and IMD pathways; bed bugs; defensin antimicrobial peptides; hematophagy; humoral innate immunity; immunization; pathogens; vectors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Balster C.B. Master’s Thesis. Wright State University; Dayton, OH, USA: 2011. The Non-Infectious Disease Implications of Bed Bug Infestations.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

