Inhibitory Effect of Bacterial Lysates Extracted from Pediococcus acidilactici on the Differentiation of 3T3-L1 Pre-Adipocytes
- PMID: 36232912
- PMCID: PMC9570163
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231911614
Inhibitory Effect of Bacterial Lysates Extracted from Pediococcus acidilactici on the Differentiation of 3T3-L1 Pre-Adipocytes
Abstract
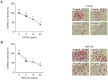
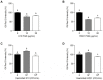
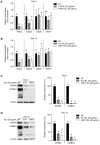
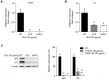
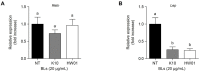
Postbiotics, including bacterial lysates, are considered alternatives to probiotics. The aim of the current study was to investigate the effect of bacterial lysates (BLs) extracted from Pediococcus acidilactici K10 (K10 BL) and P. acidilactici HW01 (HW01 BL) on the differentiation of 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes. Both K10 and HW01 BLs significantly reduced the accumulation of lipid droplets and the amounts of cellular glycerides in 3T3-L1 cells (p < 0.05). However, another postbiotic molecule, peptidoglycan of P. acidilactici K10 and P. acidilactici HW01, moderately inhibited the accumulation of lipid droplets, whereas heat-killed P. acidilactici did not effectively inhibit the lipid accumulation. The mRNA and protein levels of the transcription factors, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α, responsible for the differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells, were significantly inhibited by K10 BL and HW01 BL (p < 0.05). Both K10 and HW01 BLs decreased adipocyte-related molecules, adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein and lipoprotein lipase, at the mRNA and protein levels. Furthermore, both K10 and HW01 BLs also downregulated the mRNA expression of leptin, but not resistin. Taken together, these results suggest that P. acidilactici BLs mediate anti-adipogenic effects by inhibiting adipogenic-related transcription factors and their target molecules.
Keywords: Pediococcus acidilactici; adipogenesis; bacterial lysates; postbiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Suppression of adipocyte differentiation and lipid accumulation by stearidonic acid (SDA) in 3T3-L1 cells.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Sep 25;16(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0574-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28946872 Free PMC article.
-
6-gingerol inhibits rosiglitazone-induced adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Phytother Res. 2014 Feb;28(2):187-92. doi: 10.1002/ptr.4976. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Phytother Res. 2014. PMID: 23519881
-
Inhibition of Lipid Accumulation and Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Differentiating 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes by Pazopanib, a Multikinase Inhibitor.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 5;22(9):4884. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094884. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34063048 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-375 promotes 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation through modulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase signalling.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011 Apr;38(4):239-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05493.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21291493 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylated glucosamine inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.J Nutr Biochem. 2010 May;21(5):438-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.01.018. Epub 2009 May 7. J Nutr Biochem. 2010. PMID: 19427183
Cited by
-
Inhibition Effect of Adipogenesis and Lipogenesis via Activation of AMPK in Preadipocytes Treated with Canavalia gladiata Extract.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 20;24(3):2108. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032108. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768430 Free PMC article.
-
Indigenous-based probiotic beverage from peanuts and soybean: development, optimization, and characterization.FEMS Microbes. 2025 May 31;6:xtaf006. doi: 10.1093/femsmc/xtaf006. eCollection 2025. FEMS Microbes. 2025. PMID: 40585391 Free PMC article.
-
Heat-Inactivated Pediococcus acidilactici pA1c®HI Maintains Glycemic Control and Prevents Body Weight Gain in High-Fat-Diet-Fed Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 3;26(13):6408. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136408. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barros C.P., Guimarães J.T., Esmerino E.A., Duarte M.C.K., Silva M.C., Silva R., Ferreira B.M., Sant’Ana A.S., Freitas M.Q., Cruz A.G. Paraprobiotics and postbiotics: Concepts and potential applications in dairy products. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020;32:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2019.12.003. - DOI
-
- Aguilar-Toalá J., Garcia-Varela R., Garcia H., Mata-Haro V., González-Córdova A., Vallejo-Cordoba B., Hernández-Mendoza A. Postbiotics: An evolving term within the functional foods field. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018;75:105–114. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2018.03.009. - DOI
-
- Salminen S., Collado M.C., Endo A., Hill C., Lebeer S., Quigley E.M., Sanders M.E., Shamir R., Swann J.R., Szajewska H. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021;18:649–667. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00440-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

