Protective Effect of Rutin on Triethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate-Induced Toxicity through the Inhibition of Caspase Activation and Reactive Oxygen Species Generation in Macrophages
- PMID: 36233071
- PMCID: PMC9570090
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231911773
Protective Effect of Rutin on Triethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate-Induced Toxicity through the Inhibition of Caspase Activation and Reactive Oxygen Species Generation in Macrophages
Abstract
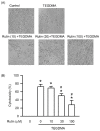
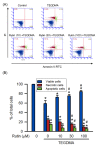
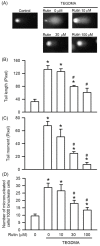
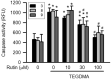
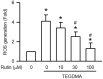
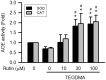
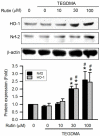
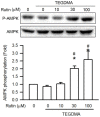
Rutin, also called quercetin-3-rhamnosyl glucoside, is a natural flavonol glycoside present in many plants. Rutin is used to treat various diseases, such as inflammation, diabetes, and cancer. For polymeric biomaterials, triethylene glycol dimethacrylate (TEGDMA) is the most commonly used monomer and serves as a restorative resin, a dentin bonding agent and sealant, and a bone cement component. Overall, TEGDMA induces various toxic effects in macrophages, including cytotoxicity, apoptosis, and genotoxicity. The aim of this study was to investigate the protective mechanism of rutin in alleviating TEGDMA-induced toxicity in RAW264.7 macrophages. After treatment with rutin, we assessed the cell viability and apoptosis of TEGDMA-induced RAW264.7 macrophages using an methylthiazol tetrazolium (MTT) assay and Annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide assay, respectively. Subsequently, we assessed the level of genotoxicity using comet and micronucleus assays, assessed the cysteinyla aspartate specific proteinases (caspases) and antioxidant enzyme (AOE) activity using commercial kits, and evaluated the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) using a dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) assay. We evaluated the expression of heme oxygenase (HO)-1, the expression of nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor (Nrf-2), and phosphorylation of AMP activated protein kinase (AMPK) using the Western blot assay. The results indicated that rutin substantially reduced the level of cytotoxicity, apoptosis, and genotoxicity of TEGDMA-induced RAW264.7 macrophages. Rutin also blocked the activity of caspase-3, caspase-8, and caspase-9 in TEGDMA-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. In addition, it decreased TEGDMA-induced ROS generation and AOE deactivation in macrophages. Finally, we found that TEGDMA-inhibited slightly the HO-1 expression, Nrf-2 expression, and AMPK phosphorylation would be revered by rutin. In addition, the HO-1 expression, Nrf-2 expression, and AMPK phosphorylation was enhanced by rutin. These findings indicate that rutin suppresses TEGDMA-induced caspase-mediated toxic effects through ROS generation and antioxidative system deactivation through the Nrf-2/AMPK pathway. Therefore, rutin has the potential to serve as a novel antitoxicity agent for TEGDMA in RAW264.7 macrophages.
Keywords: TEGDMA; antioxidant system; apoptosis; cytotoxicity; genotoxicity; macrophage; reactive oxygen species; rutin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

