HOTAIR/miR-203/CAV1 Crosstalk Influences Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in the Breast Cancer Cell
- PMID: 36233075
- PMCID: PMC9569926
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231911755
HOTAIR/miR-203/CAV1 Crosstalk Influences Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in the Breast Cancer Cell
Abstract
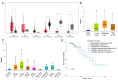
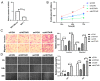
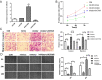
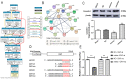
In recent years, malignant breast cancer metastasis has caused a great increase in mortality. Research on the genetic and molecular mechanisms of malignant breast cancer has continued to deepen, and targeted therapy has become the general trend. Among them, competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA)-related molecules have received much attention. Homeobox transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) has been reported to function extensively as a ceRNA in breast cancer. Notably, miR-203 and Caveolin 1 (CAV1) have also been found to play a role in breast cancer. However, the relationship between the three remains unclear. In this study, we present a new mechanic through bioinformatics tool and basic experiments: the HOTAIR/miR-203/CAV1 axis, which complemented the role network of HOTAIR as a ceRNA, thus, it will provide a novel potential idea for breast cancer research and therapy.
Keywords: CAV1; HOTAIR; breast cancer; ceRNA; invasion; miR-203; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits invasion and migration of oesophageal cancer cells via up-regulation of microRNA-204.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Oct;23(10):6595-6610. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14502. Epub 2019 Aug 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31389660 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR promotes breast cancer development through the lncRNA HOTAIR/miR-1/GOLPH3 axis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 Dec;25(12):3420-3430. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03197-3. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37099061
-
Downregulation of Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR and EZH2 Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Human Breast Cancer Cells.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2018 Aug;33(6):241-251. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2017.2432. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2018. Retraction in: Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2021 Dec;36(10):890. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2017.2432.retract. PMID: 30048163 Retracted.
-
Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR promotes medulloblastoma growth, migration and invasion by sponging miR-1/miR-206 and targeting YY1.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Apr;124:109887. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109887. Epub 2020 Jan 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31986414
-
Caveolin-1: a multifaceted driver of breast cancer progression and its application in clinical treatment.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Feb 27;12:1539-1552. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S191317. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 30881011 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing the potential of long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer: from etiology to treatment resistance and clinical applications.Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 5;14:1337579. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1337579. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38505593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The diagnostic and prognostic significance of HOXC13-AS and its molecular regulatory mechanism in human cancer.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Feb 6;12:1540048. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1540048. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 39981436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HOTAIR: a potential metastatic, drug-resistant and prognostic regulator of breast cancer.Mol Cancer. 2023 Mar 30;22(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01765-3. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36997931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-510 mediated negative regulation of Caveolin-1 in fibroblasts promotes aggressive tumor growth.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 25;14:1116644. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1116644. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37822942 Free PMC article.
-
Silence of HOTAIR promotes osteogenic differentiation and accelerates distraction osteogenesis by mediating FTO ubiquitination.J Orthop Translat. 2025 Jan 20;50:248-256. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.12.001. eCollection 2025 Jan. J Orthop Translat. 2025. PMID: 39895868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rinn J.L., Kertesz M., Wang J.K., Squazzo S.L., Xu X., Brugmann S.A., Goodnough L.H., Helms J.A., Farnham P.J., Segal E., et al. Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2007;129:1311–1323. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Collina F., Aquino G., Brogna M., Cipolletta S., Buonfanti G., De Laurentiis M., Di Bonito M., Cantile M., Botti G. LncRNA HOTAIR up-regulation is strongly related with lymph nodes metastasis and LAR subtype of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. J. Cancer. 2019;10:2018–2024. doi: 10.7150/jca.29670. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 31860317, No. 32160169/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No. 20212ACB206040/Key Project of Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- No. 20202BAB206056/National natural science foundation of Jiangxi province
- No. XMMC-FCTM202103/Key laboratory of functional and clinical translational medicine, Fujian province university
- No.202110403005, No. S202210403004/College students innovation training program of Nanchang University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

