Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Is Associated with Postprandial Anxiety Decrease in Healthy Adult Women
- PMID: 36233100
- PMCID: PMC9569757
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231911798
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Is Associated with Postprandial Anxiety Decrease in Healthy Adult Women
Abstract
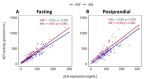
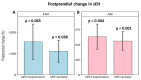
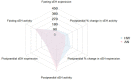
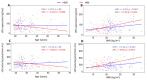
The metabolism of bioactive oxylipins by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) plays an important role in inflammation, and sEH may be a risk modifier in various human diseases and disorders. The relationships that sEH has with the risk factors of these diseases remain elusive. Herein, sEH protein expression and activity in white blood cells were characterized before and after a high-fat meal in healthy women (HW) and women with anorexia nervosa (AN). sEH expression and sEH activity were significantly correlated and increased in both groups two hours after consumption of the study meal. Fasting sEH expression and activity were positively associated with body mass index (BMI) in both groups, while an inverse association with age was found in AN only (p value < 0.05). sEH was not associated with anxiety or depression in either group at the fasting timepoint. While the anxiety score decreased after eating in both groups, a higher fasting sEH was associated with a lower postprandial anxiety decrease in HW (p value < 0.05). sEH characterization using direct measurements verified the relationship between the protein expression and in vivo activity of this important oxylipin modulator, while a well-controlled food challenge study design using HW and a clinical control group of women with disordered eating elucidated sEH’s role in the health of adult women.
Keywords: anxiety; healthy adults; metabolism; soluble epoxide hydrolase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures