Mid-Term Results of Fenestrated Endovascular Repair after Prior Open Aortic Reconstruction
- PMID: 36233467
- PMCID: PMC9571734
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11195596
Mid-Term Results of Fenestrated Endovascular Repair after Prior Open Aortic Reconstruction
Abstract
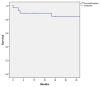
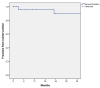
This study aims to assess the mid-term results of fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair (FEVAR) for the treatment of proximal aortic pathology after previous open surgical repair (OSR). All patients with a previous history of OSR of an abdominal aortic aneurysm undergoing a FEVAR procedure between October 2010 and November 2021 were included. The endpoints of the study were technical success, mortality, target vessel patency and reinterventions during follow-up. Thirty-five patients (34 male, mean age 72.9 ± 7 years) were included. The median interval from the primary surgery to the FEVAR procedure was 136 months (range 47-261). The indication for treatment was a para-anastomotic aneurysm in 18 (51%) patients and a true aneurysm due to progression of disease in 17 (49%) patients. Technical success was achieved in 33 (94%) patients. There was one (3%) early death due to postoperative bleeding from a renal artery. Estimated survival at 12, 24 and 36 months was 89.1% ± 6%, 84.4% ± 7.3% and 84.4% ± 7.3%, respectively. There was no aneurysm-related mortality. One (3%) target vessel occluded during follow-up and three (9%) patients underwent late reinterventions. In conclusion, FEVAR is a safe and effective alternative for the endovascular treatment of para-anastomotic aneurysms/pseudoaneurysms after OSR showing high technical success, low mortality and morbidity, and good mid-term outcomes.
Keywords: abdominal aortic aneurysm; endovascular procedures; fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair; juxtarenal aortic aneurysm; para-anastomotic aneurysm; previous aortic repair.
Conflict of interest statement
Eric LG Verhoeven has received research grants from Cook Inc., and honoraria as a speaker and consultant from Cook Inc, W.L. Gore & Ass, Maquet-Getinge, Bentley InnoMed and Siemens Healthineers. Athanasios Katsargyris has received honoraria as a speaker for Cook Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fenestrated endovascular grafts for the repair of juxtarenal aortic aneurysms: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009;9(4):1-51. Epub 2009 Jul 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009. PMID: 23074534 Free PMC article.
-
Fenestrated-Branch Endovascular Repair After Prior Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021 Nov;62(5):728-737. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2021.07.003. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 34474963
-
Open surgical repair of juxtarenal abdominal aortic aneurysms in the elderly is not associated with increased thirty-day mortality compared with fenestrated endovascular grafting.J Vasc Surg. 2021 Apr;73(4):1139-1147. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2020.08.121. Epub 2020 Sep 9. J Vasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 32919026
-
Fenestrated endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair in octogenarians is associated with higher mortality and an increased incidence of nonhome discharge.J Vasc Surg. 2022 Jun;75(6):1846-1854.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2022.01.076. Epub 2022 Jan 26. J Vasc Surg. 2022. PMID: 35090994 Review.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of endovascular juxtarenal aortic aneurysm repair demonstrates lower perioperative mortality compared with open repair.J Vasc Surg. 2019 Dec;70(6):2054-2064.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2019.04.464. Epub 2019 Jul 18. J Vasc Surg. 2019. PMID: 31327612
Cited by
-
The Ongoing Evolution of Abdominal Aortic Surgery.J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 30;12(1):302. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010302. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36615104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dangas G., O’Connor D., Firwana B., Brar S., Ellozy S., Vouyouka A., Arnold M.E., Kosmas C., Krishnan P., Wiley J., et al. Open versus endovascular stent graft repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2012;5:1071–1080. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2012.06.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Verhoeven E., Muhs B., Zeebregts C., Tielliu I., Prins T., Bos W., Oranen B., Moll F., Dungen J.V.D. Fenestrated and branched stent-grafting after previous surgery provides a good alternative to open redo surgery. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2007;33:84–90. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2006.06.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- D’Oria M., Budtz-Lilly J., Lindstrom D., Lundberg G., Jonsson M., Wanhainen A., Mani K., Unosson J. Comparison of early and mid-term outcomes after fenestrated-branched endovascular aortic repair in patients with or without prior infrarenal Repair. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2021;29:544–554. doi: 10.1177/15266028211058686. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

