Effects of Nanobubbles in Dermal Delivery of Drugs and Cosmetics
- PMID: 36234414
- PMCID: PMC9565345
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12193286
Effects of Nanobubbles in Dermal Delivery of Drugs and Cosmetics
Abstract
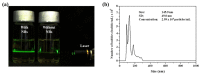
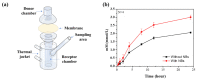
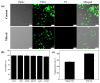
Dermal delivery, which delivers drugs and cosmetics through the skin, has attracted significant attention due to its non-invasive and simple administration compared with oral or injectable administration. However, delivery of the ingredients through the skin barrier is difficult because the primary function of the skin is to protect the human body by preventing the invasion of contaminants. Although various techniques have been developed to overcome skin barriers, chemical toxicity, complicated processes, and expensive equipment still remain as obstacles. Moreover, green chemistry, which minimizes or eliminates the use of toxic chemicals, is required in the cosmetic industry. Thus, the development of a new method for dermal delivery is required. In this study, we provide a new method for dermal delivery using nanobubbles (NBs). NBs generated in oil improve the delivery effect of the active ingredients through the high Brownian motion and charge-balancing effect. Franz cell experiments and depigmentation experiments using the B16F10 melanoma cells were conducted to confirm the enhanced delivery effects. The system using NBs will contribute to the advancement of the dermal delivery of drugs and cosmetics.
Keywords: cosmetics; depigmentation; dermal delivery; nanobubbles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effect of Nanobubbles on Transdermal Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Sep 20;13(18):2600. doi: 10.3390/nano13182600. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37764629 Free PMC article.
-
A novel dermal delivery system using natural spicules for cosmetics and therapeutics.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022 Oct;21(10):4754-4764. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14771. Epub 2022 Feb 1. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35034416
-
Final report of the safety assessment of L-Ascorbic Acid, Calcium Ascorbate, Magnesium Ascorbate, Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate, Sodium Ascorbate, and Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate as used in cosmetics.Int J Toxicol. 2005;24 Suppl 2:51-111. doi: 10.1080/10915810590953851. Int J Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 16154915 Review.
-
Final report of the safety assessment of Alcohol Denat., including SD Alcohol 3-A, SD Alcohol 30, SD Alcohol 39, SD Alcohol 39-B, SD Alcohol 39-C, SD Alcohol 40, SD Alcohol 40-B, and SD Alcohol 40-C, and the denaturants, Quassin, Brucine Sulfate/Brucine, and Denatonium Benzoate.Int J Toxicol. 2008;27 Suppl 1:1-43. doi: 10.1080/10915810802032388. Int J Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18569160 Review.
-
Current Advances of Nanocarrier Technology-Based Active Cosmetic Ingredients for Beauty Applications.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021 Jul 13;14:867-887. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S313429. eCollection 2021. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34285534 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Nanobubbles on Transdermal Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Sep 20;13(18):2600. doi: 10.3390/nano13182600. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37764629 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Study on Long-acting Nanobubbles: Current Advancement and Prospects on Theranostic Properties.Adv Pharm Bull. 2024 Jul;14(2):278-301. doi: 10.34172/apb.2024.042. Epub 2024 Mar 17. Adv Pharm Bull. 2024. PMID: 39206408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bubble-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Next-Generation Diagnosis to Therapy.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Jul 17;14(7):373. doi: 10.3390/jfb14070373. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37504868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modifications of Nanobubble Therapy for Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 2;25(13):7292. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137292. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Ultrafine Bubble Water on Gut Microbiota Composition and Health Markers in Rats.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Aug 5;15(15):1193. doi: 10.3390/nano15151193. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40801731 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim B., Cho H.-E., Moon S.H., Ahn H.-J., Bae S., Cho H.-D., An S. Transdermal delivery systems in cosmetics. Biomed. Dermatol. 2020;4:10. doi: 10.1186/s41702-020-0058-7. - DOI
-
- Montenegro L., Lai F., Offerta A., Sarpietro M.G., Micicchè L., Maccioni A.M., Valenti D., Fadda A.M. From nanoemulsions to nanostructured lipid carriers: A relevant development in dermal delivery of drugs and cosmetics. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016;32:100–112. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2015.10.003. - DOI
-
- Torin Huzil J., Sivaloganathan S., Kohandel M., Foldvari M. Drug delivery through the skin: Molecular simulations of barrier lipids to design more effective noninvasive dermal and transdermal delivery systems for small molecules, biologics, and cosmetics. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2011;3:449–462. doi: 10.1002/wnan.147. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ali S., Shabbir M., Shahid N. The Structure of Skin and Transdermal Drug Delivery System—A Review. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2015;8:103–109. doi: 10.5958/0974-360X.2015.00019.0. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

