Molecular Dynamics and Structure of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Chains Grafted from Barium Titanate Nanoparticles
- PMID: 36234912
- PMCID: PMC9571223
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27196372
Molecular Dynamics and Structure of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Chains Grafted from Barium Titanate Nanoparticles
Abstract
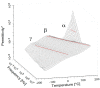
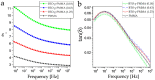
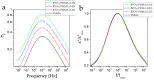
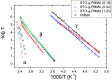
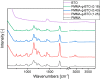
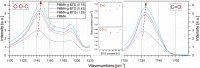
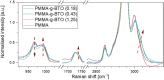
Core-shell nanocomposites comprising barium titanate, BaTiO3 (BTO), and poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) chains grafted from its surface with varied grafting densities were prepared. BTO nanocrystals are high-k inorganic materials, and the obtained nanocomposites exhibit enhanced dielectric permittivity, as compared to neat PMMA, and a relatively low level of loss tangent in a wide range of frequencies. The impact of the molecular dynamics, structure, and interactions of the BTO surface on the polymer chains was investigated. The nanocomposites were characterized by broadband dielectric and vibrational spectroscopies (IR and Raman), transmission electron microscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, and nuclear magnetic resonance. The presence of ceramic nanoparticles in core-shell composites slowed down the segmental dynamic of PMMA chains, increased glass transition temperature, and concurrently increased the thermal stability of the organic part. It was also evidenced that, in addition to segmental dynamics, local β relaxation was affected. The grafting density influenced the self-organization and interactions within the PMMA phase, affecting the organization on a smaller size scale of polymeric chains. This was explained by the interaction of the exposed surface of nanoparticles with polymer chains.
Keywords: dielectric properties; molecular dynamics; nanocomposites; polymer brushes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Baek Y., Li X., Kim N., Park C.E., An T.K., Kim J., Kim S.H. A critical role of amphiphilic polymers in organic-inorganic hybrid sol-gel derived gate dielectrics for flexible organic thin-film transistors. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2019;7:11612–11620. doi: 10.1039/C8TC06625F. - DOI
-
- Jung J.M., Kim D.H., Hur J.S., Kim H.A., Kim J.O., Jeong J.K. Acrylate-based nanocomposite zirconium-dispersed polymer dielectric for flexible oxide thin-film transistors with a curvature radius of 2 Mm. Org. Electron. 2021;98:106302. doi: 10.1016/j.orgel.2021.106302. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UMO-2014/14/A/ST5/00204/National Science Centre, Poland
- No. 685451/LaSensA, M-ERA. NET 2 scheme (European Union's Horizon 2020 research and inno-vation programme
- No. S-M-ERA. NET-21-2/Research Council of Lithuania (LMTLT)
- No. 2020/02/Y/ST5/0008/the National Science Centre of Poland
- grant No. 100577922/Saxon State Ministry for Science, Culture and Tourism (Germany)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

