Artemisia Species with High Biological Values as a Potential Source of Medicinal and Cosmetic Raw Materials
- PMID: 36234965
- PMCID: PMC9571683
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27196427
Artemisia Species with High Biological Values as a Potential Source of Medicinal and Cosmetic Raw Materials
Abstract
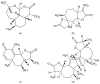
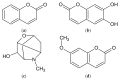
Artemisia species play a vital role in traditional and contemporary medicine. Among them, Artemisia abrotanum, Artemisia absinthium, Artemisia annua, Artemisia dracunculus, and Artemisia vulgaris are the most popular. The chemical composition and bioactivity of these species have been extensively studied. Studies on these species have confirmed their traditional applications and documented new pharmacological directions and their valuable and potential applications in cosmetology. Artemisia ssp. primarily contain sesquiterpenoid lactones, coumarins, flavonoids, and phenolic acids. Essential oils obtained from these species are of great biological importance. Extracts from Artemisia ssp. have been scientifically proven to exhibit, among others, hepatoprotective, neuroprotective, antidepressant, cytotoxic, and digestion-stimulating activities. In addition, their application in cosmetic products is currently the subject of several studies. Essential oils or extracts from different parts of Artemisia ssp. have been characterized by antibacterial, antifungal, and antioxidant activities. Products with Artemisia extracts, essential oils, or individual compounds can be used on skin, hair, and nails. Artemisia products are also used as ingredients in skincare cosmetics, such as creams, shampoos, essences, serums, masks, lotions, and tonics. This review focuses especially on elucidating the importance of the most popular/important species of the Artemisia genus in the cosmetic industry.
Keywords: Artemisia abrotanum; Artemisia absinthium; Artemisia annua; Artemisia dracunculus; Artemisia vulgaris; chemical composition; cosmetic applications; pharmacological activities; safety of use.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Podbielkowski Z., Sudnik-Wójcikowska B. Słownik Roślin Użytkowych. Państwowe Wydawnictwo Rolnicze i Leśne; Warszawa, Poland: 2003. Wydanie VI. (In Polish)
-
- Aglarova A.M., Zilfikarov I.N., Severtseva O.V. Biological characteristics and useful properties of tarragon (Artemisia dracunculus L.) (review) Pharm. Chem. J. 2008;42:81–86. doi: 10.1007/s11094-008-0064-3. - DOI
-
- Ashraf I., Zubair M., Rizwan K., Rasool N., Jamil M., Khan S.A., Tareen R.B., Ahmad V.U., Mahmood A., Riaz M., et al. Chemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial potential of essential oils from different parts of Daphne mucronata Royle. Chem. Cent. J. 2018;12:135. doi: 10.1186/s13065-018-0495-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rasool N., Afzal S., Riaz M., Rashid U., Rizwan K., Zubair M., Ali S., Shahid M. Evaluation of antioxidant activity, cytotoxic studies and GC-MS profiling of Matthiola incana (Stock flower) Legum. Res. 2013;36:21–32.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

