Methane Production Characteristics of an Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Pig Manure and Fermented Liquid Feed
- PMID: 36235045
- PMCID: PMC9572587
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27196509
Methane Production Characteristics of an Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Pig Manure and Fermented Liquid Feed
Abstract
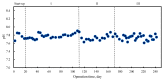
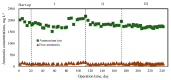
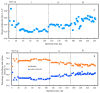
Methane production characteristics of anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure (PM) and fermented liquid feed (FLF) were investigated in a continuous digester under mesophilic conditions. The experiment followed three phases. PM alone was digested in phase I. In phases II and III, PM and FLF were mixed in a ratio of 95:5 and 90:10 (% v/v), respectively. The specific methane yields (SMYs) during phases I, II, and III were 238, 278, and 326.8 mLCH4·gVS-1-added, respectively. It was due to the effect of balancing the feedstock carbon-to-nitrogen ratio by adding FLF. This improvement can also be attributed to the readily biodegradable compounds in the FLF. The higher SMY obtained in this study showed a positive synergistic effect in the anaerobic co-digestion of PM and FLF. The results also indicate that adding the FLF positively affected and maintained a constant pH level, avoiding volatile fatty acid accumulation and ammonia inhibition in the anaerobic digestion (AD). Thus, this study provides valuable information regarding the usage of unused or wasted FLF as a co-substrate for the practical AD of PM. The production of fermented liquid additives such as FLF to improve the methane production from the AD of PM is a potential novel alternative to food waste recycling in Japan, besides compost and animal feeding.
Keywords: anaerobic co-digestion; co-substrate; fermented liquid feed; methane production; pig manure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ministry of the Environment MOE Discloses the Estimated Amount of Japan’s Food Loss and Waste Generated in FY 2018. [(accessed on 13 July 2022)];2021 Available online: https://www.env.go.jp/en/headline/2515.html.
-
- Sugiura K., Yamatani S., Watahara M., Onodera T. Ecofeed, animal feed produced from recycled food waste. Vet. Ital. 2009;45:397–404. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

