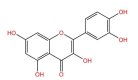
Quercetin: Its Antioxidant Mechanism, Antibacterial Properties and Potential Application in Prevention and Control of Toxipathy
- PMID: 36235082
- PMCID: PMC9571766
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27196545
Quercetin: Its Antioxidant Mechanism, Antibacterial Properties and Potential Application in Prevention and Control of Toxipathy
Abstract
Quercetin, as a flavonol compound found in plants, has a variety of biological activities. It is widely present in nature and the human diet, with powerful oxidative properties and biological activities. In this review, the antioxidant mechanism and broad-spectrum antibacterial properties of quercetin are revealed; the intervention effects of quercetin on pesticide poisoning and the pathway of action are investigated; the toxic effects of main mycotoxins on the collection and the detoxification process of quercetin are summarized; whether it is able to reduce the toxicity of mycotoxins is proved; and the harmful effects of heavy metal poisoning on the collection, the prevention, and control of quercetin are evaluated. This review is expected to enrich the understanding of the properties of quercetin and promote its better application in clinical practice.
Keywords: antioxidant; quercetin; toxipathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
-
- Nakamura T., Kinjo C., Nakamura Y., Kato Y., Nishikawa M., Hamada M., Nakajima N., Ikushiro S., Murota K. Lymphatic metabolites of quercetin after intestinal administration of quercetin-3-glucoside and its aglycone in rats. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018;645:126–136. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2018.03.024. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical