Factors Influencing the Bioavailability of Organic Molecules to Bacterial Cells-A Mini-Review
- PMID: 36235114
- PMCID: PMC9570905
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27196579
Factors Influencing the Bioavailability of Organic Molecules to Bacterial Cells-A Mini-Review
Abstract
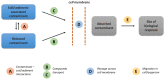
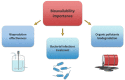
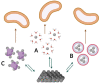
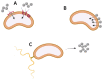
The bioavailability of organic compounds to bacterial cells is crucial for their vital activities. This includes both compounds that are desirable to the cells (e.g., sources of energy, carbon, nitrogen, and other nutrients) and undesirable compounds that are toxic to the cells. For this reason, bioavailability is an issue of great importance in many areas of human activity that are related to bacteria, e.g., biotechnological production, bioremediation of organic pollutants, and the use of antibiotics. This article proposes a classification of factors determining bioavailability, dividing them into factors at the physicochemical level (i.e., those related to the solubility of a chemical compound and its transport in aqueous solution) and factors at the microbiological level (i.e., those related to adsorption on the cell surface and those related to transport into the cell). Awareness of the importance of and the mechanisms governing each of the factors described allows their use to change bioavailability in the desired direction.
Keywords: availability; bacteria; membranes; organic chemicals; solubility.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bioavailability of organic compounds solubilized in nonionic surfactant micelles.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011 Feb;89(3):523-34. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2938-z. Epub 2010 Oct 19. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 20957356 Review.
-
Bioavailability of xenobiotics in the soil environment.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2010;203:1-86. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-1352-4_1. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 19957116 Review.
-
Extensive sorption of organic compounds to black carbon, coal, and kerogen in sediments and soils: mechanisms and consequences for distribution, bioaccumulation, and biodegradation.Environ Sci Technol. 2005 Sep 15;39(18):6881-95. doi: 10.1021/es050191b. Environ Sci Technol. 2005. PMID: 16201609
-
[Environmental behavior of graphene and its effect on the transport and fate of pollutants in environment].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2014 Sep;25(9):2723-32. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2014. PMID: 25757328 Review. Chinese.
-
Influence of Dissolved Organic Matter on Tetracycline Bioavailability to an Antibiotic-Resistant Bacterium.Environ Sci Technol. 2015 Sep 15;49(18):10903-10. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b02158. Epub 2015 Aug 26. Environ Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 26370618
Cited by
-
Co-interaction of nitrofuran antibiotics and the saponin-rich extract on gram-negative bacteria and colon epithelial cells.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Jun 5;39(8):221. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03669-2. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37273071 Free PMC article.
-
Holistic Approaches to Plant Stress Alleviation: A Comprehensive Review of the Role of Organic Compounds and Beneficial Bacteria in Promoting Growth and Health.Plants (Basel). 2024 Feb 29;13(5):695. doi: 10.3390/plants13050695. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Bioactivity and Physicochemical Properties of Emulsions Based on Tamanu, Moringa, and Inca Inchi Oils.Foods. 2023 Dec 22;13(1):62. doi: 10.3390/foods13010062. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38201090 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput characterization of bacterial responses to complex mixtures of chemical pollutants.Nat Microbiol. 2024 Apr;9(4):938-948. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01626-9. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Nat Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38499812 Free PMC article.
-
Abiotic Degradation of the Toxin Simplexin by Soil Collected from a Pimelea-Infested Paddock.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Mar 6;17(3):124. doi: 10.3390/toxins17030124. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40137897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hobot J.A. Molecular Medical Microbiology. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2015. Bacterial Ultrastructure; pp. 7–32.
-
- Vergalli J., Bodrenko I.V., Masi M., Moynié L., Acosta-Gutiérrez S., Naismith J.H., Davin-Regli A., Ceccarelli M., van den Berg B., Winterhalter M., et al. Porins and small-molecule translocation across the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020;18:164–176. doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0294-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

