Steroid Resistance Associated with High MIF and P-gp Serum Levels in SLE Patients
- PMID: 36235275
- PMCID: PMC9573564
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27196741
Steroid Resistance Associated with High MIF and P-gp Serum Levels in SLE Patients
Abstract
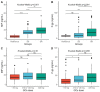
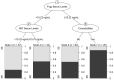
Approximately 30% of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) present steroid resistance (SR). Macrophage migration inhibition factor (MIF) and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) could be related to SR. This work aims to evaluate the relationship between MIF and P-pg serum levels in SR in SLE. Methods: Case−control study including 188 SLE patients who were divided into two groups (90 in the steroid-resistant group and 98 in the steroid-sensitive (SS) group) and 35 healthy controls. MIF and P-gp serum levels were determined by ELISA. Multivariable logistic regression and chi-squared automatic interaction detection (CHAID) were used to explore risk factors for SR. Results: The steroid-resistant group presented higher MIF and P-gp serum levels in comparison with the SS (p < 0.001) and reference (p < 0.001) groups. MIF correlated positively with P-gp (rho = 0.41, p < 0.001). MIF (≥15.75 ng/mL) and P-gp (≥15.22 ng/mL) were a risk factor for SR (OR = 2.29, OR = 5.27). CHAID identified high P-gp as the main risk factor for SR and high MIF as the second risk factor in those patients with low P-gp. Conclusions: An association between MIF and P-gp serum levels was observed in SR. CHAID identified P-gp ≥ 15.22 ng/mL as the main risk factor for SR. More studies are needed to validate these results.
Keywords: CHAID; MIF; P-gp; interaction; steroid-resistance; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New insights into the role and mechanism of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in steroid-resistant patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 May 2;14(3):R103. doi: 10.1186/ar3828. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 22551315 Free PMC article.
-
Artesunate inhibits type I interferon-induced production of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Lupus. 2017 Jan;26(1):62-72. doi: 10.1177/0961203316651738. Epub 2016 May 26. Lupus. 2017. PMID: 27230555 Free PMC article.
-
[The relationship between mRNA level of glucocorticoid receptor α, heat shock protein 90, protein level of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and glucocorticoid resistance in systemic lupus erythematosus].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2015 Nov;54(11):922-6. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26759210 Chinese.
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) as a therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019 Sep;23(9):733-744. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2019.1656718. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019. PMID: 31414920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Levels of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor and polymorphisms in systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis.Arch Med Sci. 2019 May 31;17(5):1232-1240. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2019.85459. eCollection 2021. Arch Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 34522252 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glucocorticoids, their uses, sexual dimorphisms, and diseases: new concepts, mechanisms, and discoveries.Physiol Rev. 2024 Jan 1;104(1):473-532. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00021.2023. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Physiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 37732829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: Exploring physiological roles and comparing health benefits against oncogenic and autoimmune risks (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Oct;56(4):149. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5590. Epub 2025 Jul 19. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40682854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting of oxidized Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (oxMIF) with antibody ON104 attenuates the severity of glomerulonephritis.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 7;19(10):e0311837. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311837. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39374239 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fanouriakis A., Kostopoulou M., Alunno A., Aringer M., Bajema I., Boletis J.N., Cervera R., Doria A., Gordon C., Govoni M., et al. 2019 Update of the EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019;78:736–745. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215089. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xibillé-Friedmann D., Pérez-Rodríguez M., Carrillo-Vázquez S., Álvarez-Hernández E., Aceves F.J., Ocampo-Torres M.C., García-García C., García-Figueroa J.L., Merayo-Chalico J., Barrera-Vargas A., et al. Guía de práctica clínica para el manejo del lupus eritematoso sistémico propuesta por el Colegio Mexicano de Reumatología. Reumatol. Clín. 2019;15:3–20. doi: 10.1016/j.reuma.2018.03.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pons-Estel B.A., Bonfa E., Soriano E.R., Cardiel M.H., Izcovich A., Popoff F., Criniti J.M., Vásquez G., Massardo L., Duarte M., et al. First Latin American Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Latin American Group for the Study of Lupus (GLADEL, Grupo Latino Americano de Estudio Del Lupus)–Pan-American League of Associations of Rheumatology (PANLAR) Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018;77:1549–1557. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213512. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

