Anacardium occidentale Bark as an Antidiabetic Agent
- PMID: 36235503
- PMCID: PMC9571383
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11192637
Anacardium occidentale Bark as an Antidiabetic Agent
Abstract
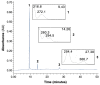
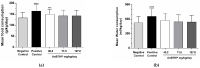
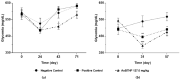
Anacardium occidentale L. is used throughout the world to treat type 2 diabetes. In Portugal, a traditional herbal preparation made with stem bark of this species (AoBTHP) has been used for more than 30 years to treat this pathology. The AoBTHP was standardized on total phenolic content, and its hypoglycemic activity was assessed using db/db mice (n = 26) for 92 days. Three doses (40.2, 71.5, and 127.0 mg/kg/day, per os) were tested, and glibenclamide (5 mg/kg/day) was used as positive control. During the study, glycemia was measured under non-fasting or fasting states. In sequence, thin-layer chromatography bioautographic assays were used for the detection of possible alpha- and beta-glucosidase inhibitors. A significant hypoglycemic effect in fasting glycemia in days 31 and 57 was observed with the three tested doses. The 71.5 mg/kg and 127.0 mg/kg AoBTHPs significantly reduced non-fasting glycemia on day 24. The highest dose showed the most significant hypoglycemic effect. Gallic acid was identified as the major alpha- and beta-glucosidase inhibitor. The 127 mg/kg/day AoBTHP dose showed a greater glucose-lowering effect than glibenclamide. For the first time, a standardized AoBTHP was tested using an in vivo diabetes model, and its usage was preclinically validated for type 2 diabetes treatment. The hypoglycemic activity of an AoBTHP can be related to the presence of alpha- and beta-glucosidase inhibitors, such as gallic acid, but other mechanisms can also be involved.
Keywords: Anacardium occidentale; alpha-glucosidase inhibitors; antidiabetic; db/db mice; gallic acid; herbal medicines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Micromorphology and Chemical Studies on Anacardium occidentale L. Stem Bark as an Herbal Medicine.Plants (Basel). 2022 Dec 20;12(1):7. doi: 10.3390/plants12010007. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36616134 Free PMC article.
-
An Integrated Approach to the Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Genotoxic Potential of Portuguese Traditional Preparations from the Bark of Anacardium occidentale L.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jan 31;13(3):420. doi: 10.3390/plants13030420. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38337956 Free PMC article.
-
Laboratory evaluation of the hypoglycemic effect of Anacardium occidentale Linn (Anacardiaceae) stem-bark extracts in rats.Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2003 Apr;25(3):199-204. doi: 10.1358/mf.2003.25.3.769640. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12743624
-
Oral antidiabetic agents: current role in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Drugs. 2005;65(3):385-411. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200565030-00005. Drugs. 2005. PMID: 15669880 Review.
-
Herbal Medicines for Diabetes Management and its Secondary Complications.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2021;17(4):437-456. doi: 10.2174/1573399816666201103143225. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2021. PMID: 33143632 Review.
Cited by
-
Octyl Gallate and Gallic Acid Isolated from Terminalia bellirica Circumvent Breast Cancer Progression by Enhancing the Intrinsic Apoptotic Signaling Pathway and Elevating the Levels of Anti-oxidant Enzymes.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023 Dec;195(12):7214-7235. doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04450-9. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36988844
-
Micromorphology and Chemical Studies on Anacardium occidentale L. Stem Bark as an Herbal Medicine.Plants (Basel). 2022 Dec 20;12(1):7. doi: 10.3390/plants12010007. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36616134 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Periploca chevalieri Browicz on Postprandial Glycemia and Carbohydrate-Hydrolyzing Enzymes.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 18;18(6):913. doi: 10.3390/ph18060913. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573309 Free PMC article.
-
An Integrated Approach to the Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Genotoxic Potential of Portuguese Traditional Preparations from the Bark of Anacardium occidentale L.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jan 31;13(3):420. doi: 10.3390/plants13030420. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38337956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mitra R., Mitchell B., Gray C., Orbell J., Coulepis T., Muralitharan M. Medicinal Plants of Brazil. Asia Pac. Biotech News. 2007;11:689–706.
-
- Orwa C., Mutua A., Kindt R., Jamnadass R., Simons A. Agroforestry Database: A Tree Reference and Selection Guide Version 4.0. [(accessed on 25 September 2022)]. Available online: http://www.worldagroforestry.org/treedb2/AFTPDFS/Anacardium_occidentale.PDF.
-
- de Carvalho Nilo Bitu V., de Carvalho Nilo Bitu V., Matias E.F.F., de Lima W.P., da Costa Portelo A., Coutinho H.D.M., de Menezes I.R.A. Ethnopharmacological Study of Plants Sold for Therapeutic Purposes in Public Markets in Northeast Brazil. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015;172:265–272. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.06.022. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Iwu M.M. Handbook of African Medicinal Plants. 2nd ed. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2014.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

