Ethnobotanical Survey of Medicinal Plants Used in the Treatment of COVID-19 and Related Respiratory Infections in Ogbomosho South and North Local Government Areas, Oyo State, Nigeria
- PMID: 36235532
- PMCID: PMC9573491
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11192667
Ethnobotanical Survey of Medicinal Plants Used in the Treatment of COVID-19 and Related Respiratory Infections in Ogbomosho South and North Local Government Areas, Oyo State, Nigeria
Abstract
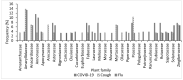
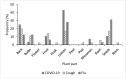
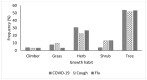
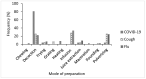
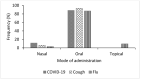
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has extensively spread worldwide with high mortality. Besides vaccination, the United States Food and Drug Administration approved only one oral medication as a treatment. Medicinal plants with antiviral and immunomodulatory properties could be explored as complementary treatments for COVID-19. Ogbomosho is home to such plants traditionally used to treat infectious diseases in Nigeria, making it relevant in complementary medicine. An ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants used to treat COVID-19 and related ailments, including cough and flu in Ogbomosho South and North Local Government Areas, Nigeria, was conducted using a semi-structured questionnaire. Information was obtained from 56 participants, consisting of different groups of individuals with native knowledge of medicinal plants, and ethnobotanical indices, including the frequency of citation (FC), relative frequency of citation (RFC), and fidelity level (FL) were computed. Twenty-six medicinal plants (17 families) were used to treat COVID-19, 31 (20 families) for cough, and 29 (19 families) for flu. The most cited plant was Zingiber officinale (FC = 10; RFC = 0.18; FL = 18%) for treating COVID-19, Citrus limon (FC = 13; RFC = 0.23; FL = 23%) for cough, and Zingiber officinale (FC = 9; RFC = 0.16; FL = 16%) for flu. Leaves were the most used plant part for treating COVID-19 and flu, while the bark was the most used for cough. Trees and herbs were the most cited plant growth forms. The herbal remedies were mostly prepared by decoction and infusion and were mainly administered orally. Further research should be conducted on the identified species for the scientific validation of their antiviral and immunomodulatory efficacies and safety for use.
Keywords: antiviral activity; drug development; ethnobotanical indices; immunomodulatory; traditional African medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- José R.J. Respiratory infections: A global burden. Ann. Res. Hosp. 2018;2:1–4. doi: 10.21037/arh.2018.09.01. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

