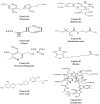
Dietary Vitamin B Complex: Orchestration in Human Nutrition throughout Life with Sex Differences
- PMID: 36235591
- PMCID: PMC9573099
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14193940
Dietary Vitamin B Complex: Orchestration in Human Nutrition throughout Life with Sex Differences
Abstract
The importance of B complex vitamins starts early in the human life cycle and continues across its different stages. At the same time, numerous reports have emphasized the critical role of adequate B complex intake. Most studies examined such issues concerning a specific vitamin B or life stage, with the majority reporting the effect of either excess or deficiency. Deep insight into the orchestration of the eight different B vitamins requirements is reviewed across the human life cycle, beginning from fertility and pregnancy and reaching adulthood and senility, emphasizing interactions among them and underlying action mechanisms. The effect of sex is also reviewed for each vitamin at each life stage to highlight the different daily requirements and/or outcomes. Thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pyridoxine, and folic acid are crucial for maternal and fetal health. During infancy and childhood, B vitamins are integrated with physical and psychological development that have a pivotal impact on one's overall health in adolescence and adulthood. A higher intake of B vitamins in the elderly is also associated with preventing some aging problems, especially those related to inflammation. All supplementation should be carefully monitored to avoid toxicity and hypervitaminosis. More research should be invested in studying each vitamin individually concerning nutritional disparities in each life stage, with extensive attention paid to cultural differences and lifestyles.
Keywords: biotin; cobalamin; folate; niacin; pantothenic acid; pyridoxine; riboflavin; thiamine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hans K.B., Jana T. Micronutrients in the life cycle: Requirements and sufficient supply. NFS J. 2018;11:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.nfs.2018.03.001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical