A Single Vitamin D3 Bolus Supplementation Improves Vitamin D Status and Reduces Proinflammatory Cytokines in Healthy Females
- PMID: 36235615
- PMCID: PMC9570631
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14193963
A Single Vitamin D3 Bolus Supplementation Improves Vitamin D Status and Reduces Proinflammatory Cytokines in Healthy Females
Abstract
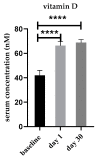
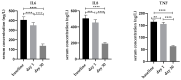
Vitamin D deficiency is a global health problem that not only leads to metabolic bone disease but also to many other illnesses, most of which are associated with chronic inflammation. Thus, our aim was to investigate the safety and effectiveness of a single high dose of vitamin D3 (80,000 IU) on vitamin D status and proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)6, IL8 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in healthy Saudi females. Fifty healthy females were recruited and orally supplemented with a single vitamin D3 bolus (80,000 IU). All participants donated fasting blood samples at baseline, one day and thirty days after supplementation. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (25(OH)D3), IL6, IL8, TNF, calcium, phosphate, parathyroid hormone (PTH) and blood lipid levels were determined. Serum 25(OH)D3 significantly increased one and thirty days after supplementation when compared with baseline without causing elevation in calcium or phosphate or a decrease in PTH to abnormal levels. In contrast, the concentrations of the three representative proinflammatory cytokines decreased gradually until the end of the study period. In conclusion, a single high dose (80,000 IU) is effective in improving serum vitamin D status and reducing the concentration of the proinflammatory cytokines in a rapid and safe way in healthy females.
Keywords: 25(OH)D3; IL6; IL8; TNF; proinflammatory cytokines; single high dose; vitamin D deficiency; vitamin D3 supplementation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Carlberg C. Chapter Ten—Molecular approaches for optimizing vitamin D supplementation. In: Litwack G., editor. Vitamins & Hormones. Volume 100. Academic Press; New York, NY, USA: 2016. pp. 255–271. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

