Melatonin Prevents Chondrocyte Matrix Degradation in Rats with Experimentally Induced Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Nuclear Factor-κB via SIRT1
- PMID: 36235621
- PMCID: PMC9571821
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14193966
Melatonin Prevents Chondrocyte Matrix Degradation in Rats with Experimentally Induced Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Nuclear Factor-κB via SIRT1
Abstract
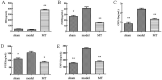
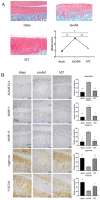
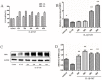
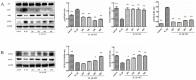
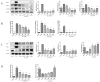
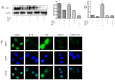
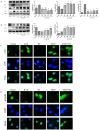
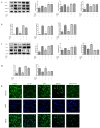
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common degenerative joint disease characterized by an imbalance of cartilage extracellular matrix (ECM) breakdown and anabolism. Melatonin (MT) is one of the hormones secreted by the pineal gland of the brain and has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-aging functions. To explore the role of MT in rats, we established an OA model in rats by anterior cruciate ligament transection (ACLT). Safranin O-fast green staining showed that intraperitoneal injection of MT (30 mg/kg) could alleviate the degeneration of articular cartilage in ACLT rats. Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis found that MT could up-regulate the expression levels of collagen type II and Aggrecan and inhibit the expression levels of matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3), matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13), and ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 4 (ADAMTS-4) in ACLT rats. To elucidate the mechanism of MT in protecting the ECM in inflammatory factor-induced rat chondrocytes, we conducted in vitro experiments by co-culturing MT with a culture medium. Western blot (WB) showed that MT could promote the expression levels of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1)/SMAD family member 2 (Smad2) and sirtuin 2-related enzyme 1 (SIRT1) and inhibit the expression of levels of phosphorylated nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibi-tor (p-p65) and phosphorylated IκB kinase-α (p-IκBα). In addition, WB and real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) results showed that MT could inhibit the expression levels of MMP-3, MMP-13, ADAMTS-4, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in chondrocytes induced by interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and up-regulate the expression of chondroprotective protein type II collagen. We found that in vivo, MT treatment protected articular cartilage in the rat ACLT model. In IL-1β-induced rat chondrocytes, MT could reduce chondrocyte matrix degradation by up-regulating nuclear factor-kB (NF-κB) signaling pathway-dependent expression of SIRT1 and protecting chondrocyte by activating the TGF-β1/Smad2 pathway.
Keywords: NF-κB pathway; SIRT1; TGF-β1/Smad2 pathway; chondrocytes; melatonin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polydatin inhibits IL-1β-mediated chondrocyte inflammation and ameliorates cartilage degradation: Involvement of the NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin pathways.Tissue Cell. 2022 Oct;78:101865. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2022.101865. Epub 2022 Jul 16. Tissue Cell. 2022. PMID: 35994920
-
Melatonin Delays Arthritis Inflammation and Reduces Cartilage Matrix Degradation through the SIRT1-Mediated NF-κB/Nrf2/TGF-β/BMPs Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 4;25(11):6202. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116202. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892389 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-Mangostin protects rat articular chondrocytes against IL-1β-induced inflammation and slows the progression of osteoarthritis in a rat model.Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Nov;52:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.08.010. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28858724
-
Ghrelin prevents articular cartilage matrix destruction in human chondrocytes.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Feb;98:651-655. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.12.050. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29291551 Review.
-
Pachymic acid suppresses the inflammatory response of chondrocytes and alleviates the progression of osteoarthritis via regulating the Sirtuin 6/NF-κB signal axis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Nov;124(Pt A):110854. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110854. Epub 2023 Aug 30. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37657246 Review.
Cited by
-
Ubiquitination and deubiquitination: Implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of osteoarthritis.J Orthop Translat. 2024 Oct 11;49:156-166. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.09.011. eCollection 2024 Nov. J Orthop Translat. 2024. PMID: 40226783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuins in intervertebral disc degeneration: current understanding.Mol Med. 2024 Mar 29;30(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00811-0. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38553713 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β3 mediates mitochondrial dynamics through the p-Smad3/AMPK pathway.Cell Prolif. 2024 May;57(5):e13579. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13579. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 38012096 Free PMC article.
-
NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Osteoarthritis: The Role of Epigenetics.Biology (Basel). 2025 Jan 14;14(1):71. doi: 10.3390/biology14010071. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39857301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential role of gut-related factors in the pathology of cartilage in osteoarthritis.Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 8;11:1515806. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1515806. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39845920 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Felson D.T., Lawrence R.C., Dieppe P.A., Hirsch R., Helmick C.G., Jordan J.M., Kington R.S., Lane N.E., Nevitt M.C., Zhang Y., et al. Osteoarthritis: New insights. Part 1: The disease and its risk factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000;133:635–646. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-133-8-200010170-00016. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

