Gallic Acid Crosslinked Gelatin and Casein Based Composite Films for Food Packaging Applications
- PMID: 36236013
- PMCID: PMC9572812
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14194065
Gallic Acid Crosslinked Gelatin and Casein Based Composite Films for Food Packaging Applications
Abstract
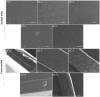
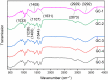
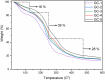
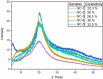
In the current work, we fabricated gelatin-casein-based edible films (GC-EFs) crosslinked with gallic acid (GA). We analyzed the physiochemical characteristics, crystallinity, thermal stability, and surface properties of the EFs using Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). It was found that the edible films possessed a semi-crystalline structure. Addition of GA enhanced the thermal stability of the edible films as well as the surface properties of the films. It was found that a higher concentration of GA (4-5% w/v) significantly improved the surface properties, observed in the surface and cross-sectional examination of SEM micrographs. EFs containing higher amounts of GA showed more compact and denser structures with smoother and more homogeneous surfaces than the control samples. In addition, swelling degree (SD), thickness, water solubility (WS), moisture content (MC), and water vapor permeability (WVP) were found to be low in EFs containing more GA concentration. Mechanical parameters revealed that the Young modulus (Ym) and tensile strength (TS) increased with a rise in GA concentration, and elongation at break (EB) reduced with a rise in GA concentration. In transparency and color analysis, it was observed that GA positively affected the transparency of the edible films.
Keywords: casein; crosslinking; edible films; gallic acid; gelatin; polymers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bonilla J., Sobral P.J. Investigation of the physicochemical, antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of gelatin-chitosan edible film mixed with plant ethanolic extracts. Food Biosci. 2016;16:17–25. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2016.07.003. - DOI
-
- Wittaya T. Protein-based edible films: Characteristics and improvement of properties. Struct. Funct. Food Eng. 2012;3:44–70.
-
- Azmin S.N.H.M., Hayat N.A.B.M., Nor M.S.M. Development and characterization of food packaging bioplastic film from cocoa pod husk cellulose incorporated with sugarcane bagasse fibre. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2020;5:248–255. doi: 10.1016/j.jobab.2020.10.003. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

