Development and Validation of an Algorithm for the Digitization of ECG Paper Images
- PMID: 36236237
- PMCID: PMC9572306
- DOI: 10.3390/s22197138
Development and Validation of an Algorithm for the Digitization of ECG Paper Images
Abstract
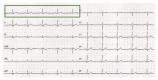
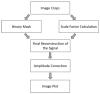
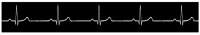
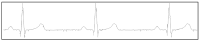
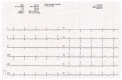
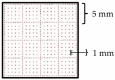
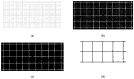
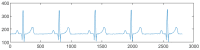
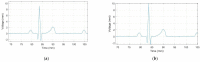
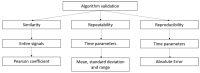
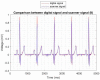
The electrocardiogram (ECG) signal describes the heart's electrical activity, allowing it to detect several health conditions, including cardiac system abnormalities and dysfunctions. Nowadays, most patient medical records are still paper-based, especially those made in past decades. The importance of collecting digitized ECGs is twofold: firstly, all medical applications can be easily implemented with an engineering approach if the ECGs are treated as signals; secondly, paper ECGs can deteriorate over time, therefore a correct evaluation of the patient's clinical evolution is not always guaranteed. The goal of this paper is the realization of an automatic conversion algorithm from paper-based ECGs (images) to digital ECG signals. The algorithm involves a digitization process tested on an image set of 16 subjects, also with pathologies. The quantitative analysis of the digitization method is carried out by evaluating the repeatability and reproducibility of the algorithm. The digitization accuracy is evaluated both on the entire signal and on six ECG time parameters (R-R peak distance, QRS complex duration, QT interval, PQ interval, P-wave duration, and heart rate). Results demonstrate the algorithm efficiency has an average Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.94 and measurement errors of the ECG time parameters are always less than 1 mm. Due to the promising experimental results, the algorithm could be embedded into a graphical interface, becoming a measurement and collection tool for cardiologists.
Keywords: ECG; Pearson’s coefficient measurement; digitization; electrocardiogram; heart pathologies; signals similarity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Cirrincione, Giansalvo, Randazzo V., Pasero E. Neural Approaches to Dynamics of Signal Exchanges. Springer; Singapore: 2020. A neural based comparative analysis for feature ex-traction from ECG signals; pp. 247–256. - DOI
-
- Sannino G., De Pietro G. A Deep Learning Approach for ECG-Based Heartbeat Classification for Arrhythmia Detection. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018;86:446–455. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2018.03.057. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

