Flow-Enhanced Photothermal Spectroscopy
- PMID: 36236246
- PMCID: PMC9570771
- DOI: 10.3390/s22197148
Flow-Enhanced Photothermal Spectroscopy
Abstract
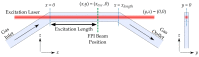
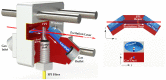
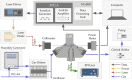
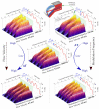
Photothermal spectroscopy (PTS) is a promising sensing technique for the measurement of gases and aerosols. PTS systems using a Fabry-Pérot interferometer (FPI) are considered particularly promising owing to their robustness and potential for miniaturization. However, limited information is available on viable procedures for signal improvement through parameter tuning. In our work, we use an FPI-based PTS configuration, in which the excitation laser irradiates the target collinearly to the flowing gas. We demonstrate that the generated thermal wave, and thus the signal intensity, is significantly affected by the ratio between excitation modulation frequency and gas flow velocity towards another. We provide an analytical model that predicts the signal intensity with particular considerations of these two parameter settings and validate the findings experimentally. The results reveal the existence of an optimal working regime, depending on the modulation frequency and flow velocity.
Keywords: Fabry–Pérot interferometer; PTS sensors; gas sensing; photothermal spectroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
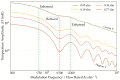
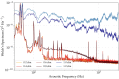
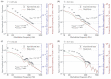
References
-
- Bialkowski S.E. Photothermal Spectroscopy Methods for Chemical Analysis. Volume 177 John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 1996.
-
- Krzempek K. A review of photothermal detection techniques for gas sensing applications. Appl. Sci. 2019;9:2826. doi: 10.3390/app9142826. - DOI
-
- Sedlacek A., Lee J. Photothermal interferometric aerosol absorption spectrometry. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2007;41:1089–1101. doi: 10.1080/02786820701697812. - DOI
-
- Dudzik G., Krzempek K., Abramski K., Wysocki G. Solid-state laser intra-cavity photothermal gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021;328:129072. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.129072. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

