Ultrasonic Monitoring of the Water Content in Concentrated Water-Petroleum Emulsions Using the Slope of the Phase Spectrum
- PMID: 36236335
- PMCID: PMC9572599
- DOI: 10.3390/s22197236
Ultrasonic Monitoring of the Water Content in Concentrated Water-Petroleum Emulsions Using the Slope of the Phase Spectrum
Abstract
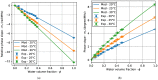
This work proposes the slope of the phase spectrum as a signal processing parameter for the ultrasonic monitoring of the water content of water-in-crude oil emulsions. Experimental measurements, with water volume fractions from 0 to 0.48 and test temperatures of 20 °C, 25 °C, and 30 °C, were carried out using ultrasonic measurement devices operating in transmission-reception and backscattering modes. The results show the phase slope depends on the water volume fraction and, to a lesser extent, on the size of the emulsion droplets, leading to a stable behavior over time. Conversely, the behavior of the phase slope as a function of the volume fraction is monotonic with low dispersion. Fitting a power function to the experimental data provides calibration curves that can be used to determine the water content with percentage relative error up to 70% for a water volume fraction of 0.06, but less than 10% for water volume fractions greater than 0.06. Furthermore, the methodology works over a wide range of volume fractions.
Keywords: backscattering; phase slope; ultrasound; volume fraction; water–petroleum emulsion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Umar A.A., Saaid I.B.M., Sulaimon A.A., Pilus R.B.M. A review of petroleum emulsions and recent progress on water-in-crude oil emulsions stabilized by natural surfactants and solids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018;165:673–690. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.03.014. - DOI
-
- Stokes D.J., Thiel B.L., Donald A.M. Direct Observation of Water-Oil Emulsion Systems in the Liquid State by Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy. Langmuir. 1998;14:4402–4408. doi: 10.1021/la980281c. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

