Point Cloud Completion Network Applied to Vehicle Data
- PMID: 36236444
- PMCID: PMC9571270
- DOI: 10.3390/s22197346
Point Cloud Completion Network Applied to Vehicle Data
Abstract
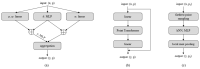
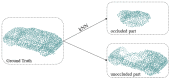
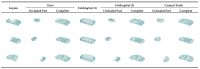
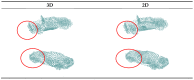
With the development of autonomous driving, augmented reality, and other fields, it is becoming increasingly important for machines to more accurately and comprehensively perceive their surrounding environment. LiDAR is one of the most important tools used by machines to obtain information about the surrounding environment. However, because of occlusion, the point cloud data obtained by LiDAR are not the complete shape of the object, and completing the incomplete point cloud shape is of great significance for further data analysis, such as classification and segmentation. In this study, we examined the completion of a 3D point cloud and improved upon the FoldingNet auto-encoder. Specifically, we used the encoder-decoder architecture to design our point cloud completion network. The encoder part uses the transformer module to enhance point cloud feature extraction, and the decoder part changes the 2D lattice used by the A network into a 3D lattice so that the network can better fit the shape of the 3D point cloud. We conducted experiments on point cloud datasets sampled from the ShapeNet car-category CAD models to verify the effectiveness of the various improvements made to the network.
Keywords: neural networks; point clouds; transformer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multi-Scope Feature Extraction for Intracranial Aneurysm 3D Point Cloud Completion.Cells. 2022 Dec 17;11(24):4107. doi: 10.3390/cells11244107. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36552872 Free PMC article.
-
Data-Driven Point Cloud Objects Completion.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Mar 28;19(7):1514. doi: 10.3390/s19071514. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30925785 Free PMC article.
-
TDNet: transformer-based network for point cloud denoising.Appl Opt. 2022 Feb 20;61(6):C80-C88. doi: 10.1364/AO.438396. Appl Opt. 2022. PMID: 35201001
-
A Survey on Deep-Learning-Based LiDAR 3D Object Detection for Autonomous Driving.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 7;22(24):9577. doi: 10.3390/s22249577. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep Learning on Point Clouds and Its Application: A Survey.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Sep 26;19(19):4188. doi: 10.3390/s19194188. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31561639 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Method of Setting the LiDAR Field of View in NDT Relocation Based on ROI.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 11;23(2):843. doi: 10.3390/s23020843. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hegde V., Zadeh R. FusionNet: 3D Object Classification Using Multiple Data Representations. arXiv. 20161607.05695
-
- Qi C.R., Su H., Mo K., Guibas L.J. PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation; Proceedings of the 30th IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); Honolulu, HI, USA. 21–26 July 2017.
-
- Wang Y., Tan D.J., Navab N., Tombari F. SoftPoolNet: Shape Descriptor for Point Cloud Completion and Classification; Proceedings of the 16th European Conference; Glasgow, UK. 23–28 August 2020.
-
- Qi C.R., Yi L., Su H., Guibas L.J. PointNet plus plus: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space; Proceedings of the 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS); Long Beach, CA, USA. 4–9 December 2017.
Grants and funding
- No. 62090054 and 61934003/the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants
- No. 2019C054-1 and 2020C019-2/Jilin Province Development and Reform Commission
- 20200501007GX and 20210301014GX/Jilin Scientific and Technological Development Program
- JLUSTIRT, 2021TD-39/Program for JLU Science and Technology Innovative Research Team
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

