[The Role of Cardiac MRI in the Diagnosis of Fabry Disease]
- PMID: 36237382
- PMCID: PMC9431820
- DOI: 10.3348/jksr.2020.81.2.302
[The Role of Cardiac MRI in the Diagnosis of Fabry Disease]
Abstract
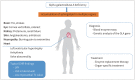
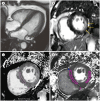
Fabry disease is a rare X-linked metabolic disorder that is characterized by the accumulation of glycosphingolipids in various organs, resulting from the deficiency of alpha-galactosidase A. Cardiac involvement is relatively common; myocardial inflammation, left ventricular hypertrophy, and myocardial fibrosis secondary to abnormal lipid deposition in myocytes are often observed. Hence, the diagnosis of cardiac involvement is crucial for evaluating patient prognosis. Cardiac MRI is the standard technique for measuring the function, volume, and mass of the ventricles. It is also useful for myocardial tissue characterizations. The evaluation of native myocardial T1 values can facilitate early diagnosis of cardiac involvement, while measurements of left ventricular myocardial mass can be used to monitor treatment outcomes, in patients with Fabry disease. Consequently, cardiac MRI can provide useful information for diagnosing, monitoring, and treating patients with Fabry disease.
파브리병(Fabry disease)은 매우 드문 X-연관 유전 대사 질환으로 알파 갈락토시다아제(alpha galactosidase A)의 결핍으로 인하여 다양한 세포 및 기관에 글리코스핑고지질(glycosphingolipid) 의 축적을 초래하는 질환이다. 심장 침범이 비교적 흔하며 비정상적인 지질침착으로 인한 심근 염증, 좌심실 비대 및 심근 섬유증을 일으킨다. 심장 침범은 환자 예후를 결정하는 중요한 요인이므로 이를 진단하는 것은 매우 중요하다. 심장 자기공명영상은 심실의 기능, 부피 측정을 위한 표준기법으로 알려져 있으며 심근의 조직 변화를 볼 수 있는 유용한 기법이다. 특히 최근 많이 쓰이는 T1 지도화 기법을 통한 심근 조영 전 T1 수치를 이용하여 파브리병의 심장 침범을 조기 진단할 수 있으며 자기공명영상을 이용한 심근 질량 측정으로 치료 모니터링을 할 수 있다. 심장 자기공명영상은 파브리병 환자에서 다양한 역할을 할 수 있을 것으로 생각되며 이에 대해 정리해보고자 한다.
Copyrights © 2020 The Korean Society of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Cardiac Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Anderson-Fabry Disease.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Jul;12(7 Pt 1):1230-1242. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.11.039. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31272606 Review.
-
The role of native T1 values on the evaluation of cardiac manifestation in Japanese Fabry disease patients.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2022 Mar 16;31:100858. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2022.100858. eCollection 2022 Jun. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2022. PMID: 35782602 Free PMC article.
-
Anderson-Fabry disease: a multiorgan disease.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(33):5974-96. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990352. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23448451 Review.
-
Anderson-fabry disease: role of traditional and new cardiac MRI techniques.Br J Radiol. 2021 Aug 1;94(1124):20210020. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20210020. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Br J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34233483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of preclinical left ventricular dysfunction in Fabry disease: the contribution of tissue Doppler.Rev Port Cardiol. 2006 Jun;25(6):613-37. Rev Port Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 17019980 English, Portuguese.
Cited by
-
Advanced CMR Techniques in Anderson-Fabry Disease: State of the Art.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Aug 4;13(15):2598. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13152598. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568960 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- El-Abassi R, Singhal D, England JD. Fabry's disease. J Neurol Sci. 2014;344:5–19. - PubMed
-
- Zarate YA, Hopkin RJ. Fabry's disease. Lancet. 2008;372:1427–1435. - PubMed
-
- Linhart A, Palecek T, Bultas J, Ferguson JJ, Hrudová J, Karetová D, et al. New insights in cardiac structural changes in patients with Fabry's disease. Am Heart J. 2000;139:1101–1108. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

