The application of network agenda setting model during the COVID-19 pandemic based on latent dirichlet allocation topic modeling
- PMID: 36237691
- PMCID: PMC9551107
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.954576
The application of network agenda setting model during the COVID-19 pandemic based on latent dirichlet allocation topic modeling
Abstract
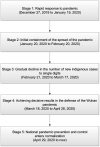
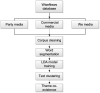
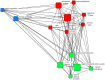
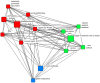
Based on Network Agenda Setting Model, this study collected 42,516 media reports from Party Media, commercial media, and We Media of China during the COVID-19 pandemic. We trained LDA models for topic clustering through unsupervised machine learning. Questionnaires (N = 470) and social network analysis methods were then applied to examine the correlation between media network agendas and public network agendas in terms of explicit and implicit topics. The study found that the media reports could be classified into 14 topics by the LDA topic modeling, and the three types of media presented homogeneity in the topics of their reports, yet had their own characteristics; there was a significant correlation between the media network agenda and the public network agenda, and the We Media reports had the most prominent effect on the public network agenda; the correlation between the media agenda and the implicit public agenda was higher than that of the explicit public agenda. Overall, findings showed a significant correlation between network agendas among different media.
Keywords: LDA topic modeling; agenda network; agenda setting; explicit public agenda; implicit public agenda.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Geng and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Mutual Influence of the World Health Organization (WHO) and Twitter Users During COVID-19: Network Agenda-Setting Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2022 Apr 26;24(4):e34321. doi: 10.2196/34321. J Med Internet Res. 2022. PMID: 35275836 Free PMC article.
-
Do news media and citizens have the same agenda on COVID-19? an empirical comparison of twitter posts.Technol Forecast Soc Change. 2021 Aug;169:120849. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120849. Epub 2021 Apr 30. Technol Forecast Soc Change. 2021. PMID: 36540545 Free PMC article.
-
Concerns Expressed by Chinese Social Media Users During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Content Analysis of Sina Weibo Microblogging Data.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Nov 26;22(11):e22152. doi: 10.2196/22152. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 33151894 Free PMC article.
-
Media Reports on COVID-19 Vaccinations: A Study of Topic Modeling in South Korea.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Dec 16;10(12):2166. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10122166. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36560577 Free PMC article.
-
News Coverage of Face Masks in Australia During the Early COVID-19 Pandemic: Topic Modeling Study.JMIR Infodemiology. 2023 Aug 16;3:e43011. doi: 10.2196/43011. JMIR Infodemiology. 2023. PMID: 37379362 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The impact and management of internet-based public opinion dissemination during emergencies: A case study of Baidu News during the first wave of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).PLoS One. 2024 Apr 4;19(4):e0299374. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299374. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38573976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apriliyanti I. D., Utomo W. P., Purwanto E. A. (2021). Examining the policy narratives and the role of the media in policy responses to the covid-19 crisis in Indonesia. J. Asian Public Policy 14, 1–17. doi: 10.1080/17516234.2021.1954770 - DOI
-
- Buturoiu D. R., Gavrilescu M. (2021). Key words associated with the covid-19 pandemic. Comparing the media and the public agenda. J. Media Res. 14, 5–25. doi: 10.24193/jmr.40.1 - DOI
-
- Chen A., Zhang X. (2021). Changing social representations and agenda interactions of gene editing after crises: a network agenda-setting study on Chinese social media. Soc. Sci. Comput. Rev. 40, 1133–1152. doi: 10.1177/0894439321998066 - DOI
-
- China Internet Network Information Center (2021). The 47th China statistical report on Internet development. Available at: http://www.cnnic.net.cn/hlwfzyj/hlwxzbg/ (Accessed August 10, 2022).
-
- Golan G., Wanta W. (2001). Second-level agenda setting in the New Hampshire primary: a comparison of coverage in three newspapers and public perceptions of candidates. J. Mass Commun. Q. 78, 247–259. doi: 10.1177/107769900107800203 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources