Characterization and subcellular localization of Alongshan virus proteins
- PMID: 36238596
- PMCID: PMC9551281
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1000322
Characterization and subcellular localization of Alongshan virus proteins
Abstract
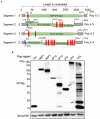
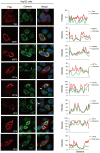
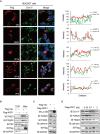
Alongshan virus (ALSV) in the Jingmenvirus group within the family Flaviviridae is a newly discovered tick-borne virus associated with human disease, whose genome includes four segments and encodes four structural proteins (VP1a, VP1b, VP2, VP3, and VP4) and two non-structural proteins (NSP1 and NSP2). Here, we characterized the subcellular distribution and potential function of ALSV proteins in host cells. We found that viral proteins exhibited diverse subcellular distribution in multiple tissue-deriving cells and induced various morphological changes in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and NSP2, VP1b, VP2, and VP4 were all co-localized in the ER. The nuclear transfer and co-localization of VP4 and calnexin (a marker protein of ER), which were independent of their interaction, were unique to HepG2 cells. Expression of NSP1 could significantly reduce mitochondria quantity by inducing mitophagy. These findings would contribute to better understanding of the pathogenesis of emerging segmented flaviviruses.
Keywords: Alongshan virus; characterization; segmented flavivirus; subcellular localization; viral proteins.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Wu, Liu, Ma, Pan, Huang, Du, Yu, Sui, Wang, Hou and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Agarwal A., Alam M. F., Basu B., Pattanayak S., Asthana S., Syed G. H., et al. (2022). Japanese encephalitis virus NS4A protein interacts with PTEN-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) and promotes mitophagy in infected cells. Microbiol. Spectr. 10:e0083022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00830-22, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

