Differential Diagnosis of Urticarial Lesions
- PMID: 36238930
- PMCID: PMC9552949
- DOI: 10.3389/falgy.2022.808543
Differential Diagnosis of Urticarial Lesions
Abstract
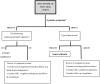
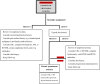
Urticaria is a mast cell-dependent disease, characterized by the presence of wheals, angioedema, or both in the absence of systemic symptoms. It is a common disease worldwide, with an important health burden especially in chronic situations, that last more than 6 weeks. Although urticaria is usually a straightforward diagnosis, some diseases presenting with urticarial lesions must be excluded, particularly urticarial vasculitis and auto-inflammatory syndromes. In these settings additional atypical features are often present (long-lasting lesions, bruising, fever, malaise, arthralgia), allowing the clinician to suspect a diagnosis other than urticaria. The authors propose an approach based on these atypical features, the presence or absence of systemic symptoms and on skin histopathology as well as some blood parameters.
Keywords: angioedema; autoinflammatory syndromes; chronic spontaneous urticaria; urticaria; urticarial syndromes.
Copyright © 2022 Matos, Figueiredo and Gonçalo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Konstantinou GN, Papadopoulos NG, Tavladaki T, Tsekoura T, Tsilimigaki A. Childhood acute urticaria in northern and southern Europe shows a similar epidemiological pattern and significant meteorological influences. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. (2011) 22(1-Part-I):36–42. 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2010.01093.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

