Adenosine receptors as emerging therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease
- PMID: 36239063
- PMCID: PMC9590297
- DOI: 10.23876/j.krcp.22.011
Adenosine receptors as emerging therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease
Abstract
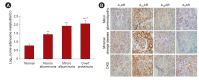
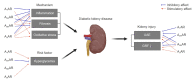
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is now a pandemic worldwide, and novel therapeutic options are urgently required. Adenosine, an adenosine triphosphate metabolite, plays a role in kidney homeostasis through interacting with four types of adenosine receptors (ARs): A1AR, A2AAR, A2BAR, and A3AR. Increasing evidence highlights the role of adenosine and ARs in the development and progression of DKD: 1) increased adenosine in the plasma and urine of diabetics with kidney injury, 2) increased expression of each of the ARs in diabetic kidneys, 3) the protective effect of coffee, a commonly ingested nonselective AR antagonist, on DKD, and 4) the protective effect of AR modulators in experimental DKD models. We propose AR modulators as a new therapeutic option to treat DKD. Detailed mechanistic studies on the pharmacology of AR modulators will help us to develop effective first-in-class AR modulators against DKD.
Keywords: Adenosine; Diabetic kidney disease; Fibrosis; Purinergic P1 receptor agonists; Purinergic P1 receptor antagonists; Purinergic P1 receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



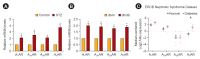
References
-
- Antonioli L, Blandizzi C, Csóka B, Pacher P, Haskó G. Adenosine signalling in diabetes mellitus--pathophysiology and therapeutic considerations. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015;11:228–241. - PubMed
-
- Dwyer KM, Kishore BK, Robson SC. Conversion of extracellular ATP into adenosine: a master switch in renal health and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16:509–524. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

