Possible expansion of Ixodes ricinus in the United Kingdom identified through the Tick Surveillance Scheme between 2013 and 2020
- PMID: 36239468
- PMCID: PMC10092138
- DOI: 10.1111/mve.12612
Possible expansion of Ixodes ricinus in the United Kingdom identified through the Tick Surveillance Scheme between 2013 and 2020
Abstract
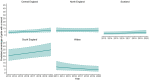
The tick Ixodes ricinus (Ixodida: Ixodidae, Linnaeus) is the main vector of several pathogens including Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. (agent of Lyme borreliosis) and tick-borne encephalitis virus. Its distribution depends on many factors including suitable habitat, climate and presence of hosts. In this study, we present records of I. ricinus bites on humans, dogs (Canis lupus familiaris; Carnivora: Canidae, L.) and cats (Felis catus; Carnivora: Felidiae, L.) in the United Kingdom (UK) obtained through the Tick Surveillance Scheme between 2013 and 2020. We divided the UK into 20 km x 20 km grids and 9.2% (range 1.2%-30%) of grids had at least one record every year since 2013. Most regions reported a yearly increase in the percentage of grids reporting I. ricinus since 2013 and the highest changes occurred in the South and East England with 5%-6.7% of new grids reporting I. ricinus bites each year in areas that never reported ticks before. Spatiotemporal analyses suggested that, while all regions recorded I. ricinus in new areas every year, there was a yearly decline in the percentage of new areas covered, except for Scotland. We discuss potential drivers of tick expansion, including reforestation and increase in deer populations.
Keywords: Borrelia burgdorferi s.l; distribution; surveillance; vector; vector-borne disease.
© 2022 Crown copyright. Medical and Veterinary Entomology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Royal Entomological Society. This article is published with the permission of the Controller of HMSO and the Queen's Printer for Scotland.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Barton, K. (2019) MuMIn: multi‐model inference. In: R package version 1.43.6. http://mumin.r-forge.r-project.org/
-
- Bates, D. , Mächler, M. , Bolker, B. & Walker, S. (2015) Fitting linear mixed‐effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67, 1–48.
-
- Benda, R. (1958) The common tick Ixodes ricinus L. as a reservoir and vector of tick‐borne encephalitis. I. Survival of the virus (strain B3) during the development of the tick under laboratory conditions. Journal of Hygiene, Epidemiology, Microbiology and Immunology, 2, 331–334.
-
- Burgdorfer, W. , Lane, R.S. , Barbour, A.G. , Gresbrink, R.A. & Anderson, J.R. (1985) The western black‐legged tick, Ixodes pacificus: a vector of Borrelia burgdorferi . The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 34, 925–930. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

