Evaluating Electrolyte-Anode Interface Stability in Sodium All-Solid-State Batteries
- PMID: 36239697
- PMCID: PMC9614718
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c12759
Evaluating Electrolyte-Anode Interface Stability in Sodium All-Solid-State Batteries
Abstract
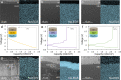
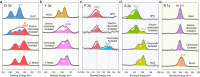
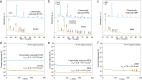
All-solid-state batteries have recently gained considerable attention due to their potential improvements in safety, energy density, and cycle-life compared to conventional liquid electrolyte batteries. Sodium all-solid-state batteries also offer the potential to eliminate costly materials containing lithium, nickel, and cobalt, making them ideal for emerging grid energy storage applications. However, significant work is required to understand the persisting limitations and long-term cyclability of Na all-solid-state-based batteries. In this work, we demonstrate the importance of careful solid electrolyte selection for use against an alloy anode in Na all-solid-state batteries. Three emerging solid electrolyte material classes were chosen for this study: the chloride Na2.25Y0.25Zr0.75Cl6, sulfide Na3PS4, and borohydride Na2(B10H10)0.5(B12H12)0.5. Focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM) imaging, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) were utilized to characterize the evolution of the anode-electrolyte interface upon electrochemical cycling. The obtained results revealed that the interface stability is determined by both the intrinsic electrochemical stability of the solid electrolyte and the passivating properties of the formed interfacial products. With appropriate material selection for stability at the respective anode and cathode interfaces, stable cycling performance can be achieved for Na all-solid-state batteries.
Keywords: anode−electrolyte interface; borohydride; chloride; sodium; solid electrolyte; sulfide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mattick C. S.; Williams E.; Allenby B. R. Historical Trends in Global Energy Consumption. IEEE Technol. Soc. Mag. 2010, 29, 22–30. 10.1109/MTS.2010.938106. - DOI
-
- Bilgen S. Structure and Environmental Impact of Global Energy Consumption. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 890–902. 10.1016/j.rser.2014.07.004. - DOI
-
- Sayahpour B.; Hirsh H.; Parab S.; Nguyen L. H. B.; Zhang M.; Meng Y. S. Perspective: Design of Cathode Materials for Sustainable Sodium-Ion Batteries. MRS Energy Sustainability 2022, 1.10.1557/s43581-022-00029-9. - DOI
-
- Hirsh H. S.; Li Y.; Tan D. H. S.; Zhang M.; Zhao E.; Meng Y. S. Sodium-Ion Batteries Paving the Way for Grid Energy Storage. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2001274.10.1002/aenm.202001274. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

