Heterogeneity of dose distribution in normal tissues in case of radiopharmaceutical therapy with alpha-emitting radionuclides
- PMID: 36239799
- PMCID: PMC9630198
- DOI: 10.1007/s00411-022-01000-5
Heterogeneity of dose distribution in normal tissues in case of radiopharmaceutical therapy with alpha-emitting radionuclides
Abstract
Heterogeneity of dose distribution has been shown at different spatial scales in diagnostic nuclear medicine. In cancer treatment using new radiopharmaceuticals with alpha-particle emitters, it has shown an extensive degree of dose heterogeneity affecting both tumour control and toxicity of organs at risk. This review aims to provide an overview of generalized internal dosimetry in nuclear medicine and highlight the need of consideration of the dose heterogeneity within organs at risk. The current methods used for patient dosimetry in radiopharmaceutical therapy are summarized. Bio-distribution and dose heterogeneities of alpha-particle emitting pharmaceutical 223Ra (Xofigo) within bone tissues are presented as an example. In line with the strategical research agendas of the Multidisciplinary European Low Dose Initiative (MELODI) and the European Radiation Dosimetry Group (EURADOS), future research direction of pharmacokinetic modelling and dosimetry in patient radiopharmaceutical therapy are recommended.
Keywords: Alpha-emitter; Dose heterogeneity; Normal tissue, bone marrow; Patient dosimetry; Radiopharmaceutical therapy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
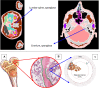
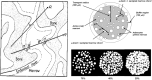
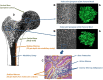
References
-
- ClinicalTrials.gov (2022) Study of 225Ac-PSMA-617 in men with PSMA-positive prostate cancer. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04597411.
-
- Adelstein SJ. Heterogeneity of dose-distribution in nuclear medicine. Proc Twenty-Eight Annu Meet NCRP Radiat Prot Med. 1993;14:122–131.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

