Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutant gliomas: A Society for Neuro-Oncology (SNO) consensus review on diagnosis, management, and future directions
- PMID: 36239925
- PMCID: PMC9825337
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/noac207
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutant gliomas: A Society for Neuro-Oncology (SNO) consensus review on diagnosis, management, and future directions
Abstract
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutant gliomas are the most common adult, malignant primary brain tumors diagnosed in patients younger than 50, constituting an important cause of morbidity and mortality. In recent years, there has been significant progress in understanding the molecular pathogenesis and biology of these tumors, sparking multiple efforts to improve their diagnosis and treatment. In this consensus review from the Society for Neuro-Oncology (SNO), the current diagnosis and management of IDH-mutant gliomas will be discussed. In addition, novel therapies, such as targeted molecular therapies and immunotherapies, will be reviewed. Current challenges and future directions for research will be discussed.
Keywords: D-2HG; Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH); glioma.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

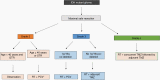
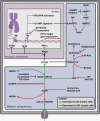
Comment in
-
Optimize treatment approaches in isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutant gliomas: open issues.Neuro Oncol. 2023 Jan 5;25(1):26-27. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noac227. Neuro Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36245275 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bailey P, Cushing H.. A Classification of the Tumors of the Glioma Group on a Histogenetic Basis with a Correlated Study of Prognosis. Philadelphia, London and Montreal: Lippincott; 1926.
-
- Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, et al. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016; 131(6):803–820. - PubMed

