Contribution of Common Genetic Variants to Risk of Early-Onset Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 36240095
- PMCID: PMC9620803
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000201006
Contribution of Common Genetic Variants to Risk of Early-Onset Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
Background and objectives: Current genome-wide association studies of ischemic stroke have focused primarily on late-onset disease. As a complement to these studies, we sought to identify the contribution of common genetic variants to risk of early-onset ischemic stroke.
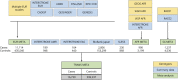
Methods: We performed a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of early-onset stroke (EOS), ages 18-59 years, using individual-level data or summary statistics in 16,730 cases and 599,237 nonstroke controls obtained across 48 different studies. We further compared effect sizes at associated loci between EOS and late-onset stroke (LOS) and compared polygenic risk scores (PRS) for venous thromboembolism (VTE) between EOS and LOS.
Results: We observed genome-wide significant associations of EOS with 2 variants in ABO, a known stroke locus. These variants tag blood subgroups O1 and A1, and the effect sizes of both variants were significantly larger in EOS compared with LOS. The odds ratio (OR) for rs529565, tagging O1, was 0.88 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.85-0.91) in EOS vs 0.96 (95% CI: 0.92-1.00) in LOS, and the OR for rs635634, tagging A1, was 1.16 (1.11-1.21) for EOS vs 1.05 (0.99-1.11) in LOS; p-values for interaction = 0.001 and 0.005, respectively. Using PRSs, we observed that greater genetic risk for VTE, another prothrombotic condition, was more strongly associated with EOS compared with LOS (p = 0.008).
Discussion: The ABO locus, genetically predicted blood group A, and higher genetic propensity for venous thrombosis are more strongly associated with EOS than with LOS, supporting a stronger role of prothrombotic factors in EOS.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures


References
-
- Malik R, Chauhan G, Traylor M, et al. , AFGen Consortium, Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology CHARGE Consortium, International Genomics of Blood Pressure iGEN-BP Consortium, INVENT Consortium, STARNET, BioBank Japan Cooperative Hospital Group, COMPASS Consortium, EPIC-CVD Consortium, EPIC-InterAct Consortium, International Stroke Genetics Consortium ISGC, METASTROKE Consortium, Neurology Working Group of the CHARGE Consortium, NINDS Stroke Genetics Network SiGN, UK Young Lacunar DNA Study, MEGASTROKE Consortium. Multiancestry genome-wide association study of 520, 000 subjects identifies 32 loci associated with stroke and stroke subtypes. Nat Genet. 2018;50(4):524-537. - PMC - PubMed
-
- MacClellan LR, Mitchell BD, Cole JW, et al. . Familial aggregation of ischemic stroke in young women: the Stroke Prevention in Young Women Study. Genet Epidemiol. 2006;30(7):602-608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MC_U137686851/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 212946/Z/18/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P30 AG028747/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12026/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 NS100178/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_14135/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 NS114045/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_00017/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 NS105150/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/S004130/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL088521/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135129/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_13049/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
