SANReSP: A new Italian questionnaire to screen patients for obstructive sleep apnea
- PMID: 36240186
- PMCID: PMC9565397
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276217
SANReSP: A new Italian questionnaire to screen patients for obstructive sleep apnea
Abstract
Purpose: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common, prevalent, and underdiagnosed disorder. Its lack of diagnosis and treatment is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Previous screening questionnaires investigated parameters including body mass index, age, neck circumference, and sex, in addition to symptoms. This study aimed to validate a new Italian, self-administered, and easy-to-use six-item questionnaire that evaluates only subjective symptoms.
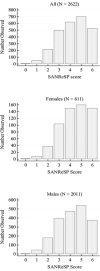
Patients and methods: The present study included 2622 patients (male, 2011; female, 611). Patients who were at least 18 years old, spoke Italian, referred to our sleep clinic for possible OSA, and completed the self-administered SANReSP questionnaire were recruited for the study. The predictive performance of the questionnaire was also evaluated.
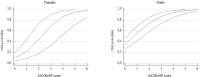
Results: Nocturnal study showed 89.9% of OSA patients had apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) ≥ 5/h; 68.7%, AHI ≥ 15/h; and 48.2%, AHI ≥ 30/h. The optimal SANReSP score for AHI ≥ 5/h was >3 with a sensitivity and specificity of 74.76% and 67.92%, respectively, and an area under receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) of 0.76. For moderate-severe OSA, the optimal SANReSP score was >3 (sensitivity, 78.18%; specificity, 46.53%; ROC, 0.66). For severe OSA, the optimal SANReSP score was >4 (sensitivity, 59.10%; specificity, 64.73%; ROC, 0.65). The probability of OSA increased with higher SANReSP scores (98.7% and 97.9% in men and women, respectively).
Conclusion: The SANReSP questionnaire is a short, easy-to-use, and self-administered screening tool for OSA. Its performance is similar to that of other widely used questionnaires; furthermore, it is advantageous in that it does not require anthropometric measurements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the Arabic version of STOP-Bang questionnaire as a screening tool for obstructive sleep apnea.Sleep Breath. 2015 Dec;19(4):1235-40. doi: 10.1007/s11325-015-1150-x. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Sleep Breath. 2015. PMID: 25758298
-
[Validation of NoSAS Score and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Hypopnea Syndrome Screening Model for Female Snorers in Females with Obstructive Sleep Apnea].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2019 Dec 30;41(6):825-831. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.11131. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31907135 Chinese.
-
[Comparison of the NoSAS score with four different questionnaires as screening tools for obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2018 Mar 12;41(3):213-219. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-0939.2018.03.013. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29518851 Chinese.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of the Berlin questionnaire, STOP-BANG, STOP, and Epworth sleepiness scale in detecting obstructive sleep apnea: A bivariate meta-analysis.Sleep Med Rev. 2017 Dec;36:57-70. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2016.10.004. Epub 2016 Nov 5. Sleep Med Rev. 2017. PMID: 27919588 Review.
-
Validation of the STOP-Bang questionnaire as a screening tool for obstructive sleep apnoea in patients with cardiovascular risk factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2021 Mar;8(1):e000848. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2020-000848. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2021. PMID: 33664122 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

