En masse organoid phenotyping informs metabolic-associated genetic susceptibility to NASH
- PMID: 36240780
- PMCID: PMC9617783
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.09.031
En masse organoid phenotyping informs metabolic-associated genetic susceptibility to NASH
Abstract
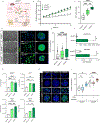
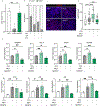
Genotype-phenotype associations for common diseases are often compounded by pleiotropy and metabolic state. Here, we devised a pooled human organoid-panel of steatohepatitis to investigate the impact of metabolic status on genotype-phenotype association. En masse population-based phenotypic analysis under insulin insensitive conditions predicted key non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)-genetic factors including the glucokinase regulatory protein (GCKR)-rs1260326:C>T. Analysis of NASH clinical cohorts revealed that GCKR-rs1260326-T allele elevates disease severity only under diabetic state but protects from fibrosis under non-diabetic states. Transcriptomic, metabolomic, and pharmacological analyses indicate significant mitochondrial dysfunction incurred by GCKR-rs1260326, which was not reversed with metformin. Uncoupling oxidative mechanisms mitigated mitochondrial dysfunction and permitted adaptation to increased fatty acid supply while protecting against oxidant stress, forming a basis for future therapeutic approaches for diabetic NASH. Thus, "in-a-dish" genotype-phenotype association strategies disentangle the opposing roles of metabolic-associated gene variant functions and offer a rich mechanistic, diagnostic, and therapeutic inference toolbox toward precision hepatology. VIDEO ABSTRACT.
Keywords: GCKR-rs1260326; NASH; de novo lipogenesis; genotype-phenotype association; human liver organoid; iPSC; mitochondrial dysfunction; population organoid panel.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests R.P.M., G.M.S., and T.T. are equity holders for The Liver Company, inc. M.Kimura and T.T. are co-inventors for the technology disclosed in the manuscript.
Figures



References
-
- Anstee QM, Darlay R, Cockell S, Meroni M, Govaere O, Tiniakos D, Burt AD, Bedossa P, Palmer J, Liu YL, et al. (2020). Genome-wide association study of non-alcoholic fatty liver and steatohepatitis in a histologically characterised cohort(). J Hepatol 73, 505–515. - PubMed
-
- Belalcazar LM, Papandonatos GD, Erar B, Peter I, Alkofide H, Balasubramanyam A, Brautbar A, Kahn SE, Knowler WC, Ballantyne CM, et al. (2016). Lifestyle Intervention for Weight Loss and Cardiometabolic Changes in the Setting of Glucokinase Regulatory Protein Inhibition: Glucokinase Regulatory Protein-Leu446Pro Variant in Look AHEAD. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 9, 71–78. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bellentani S, Scaglioni F, Marino M, and Bedogni G (2010). Epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Dis 28, 155–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

