The causes of preterm neonatal deaths in India and Pakistan (PURPOSe): a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 36240824
- PMCID: PMC9579353
- DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00384-9
The causes of preterm neonatal deaths in India and Pakistan (PURPOSe): a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Preterm birth remains the major cause of neonatal death worldwide. South Asia contributes disproportionately to deaths among preterm births worldwide, yet few population-based studies have assessed the underlying causes of deaths. Novel evaluations, including histological and bacteriological assessments of placental and fetal tissues, facilitate more precise determination of the underlying causes of preterm deaths. We sought to assess underlying and contributing causes of preterm neonatal deaths in India and Pakistan.
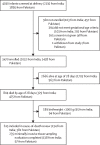
Methods: The project to understand and research preterm pregnancy outcomes and stillbirths in South Asia (PURPOSe) was a prospective cohort study done in three hospitals in Davangere, India, and two hospitals in Karachi, Pakistan. All pregnant females older than 14 years were screened at the time of presentation for delivery, and those with an expected or known preterm birth, defined as less than 37 weeks of gestation, were enrolled. Liveborn neonates with a weight of 1000 g or more who died by 28 days after birth were included in analyses. Placentas were collected and histologically evaluated. In addition, among all neonatal deaths, with consent, minimally invasive tissue sampling was performed for histological analyses. PCR testing was performed to assess microbial pathogens in the placental, blood, and fetal tissues collected. An independent panel reviewed available data, including clinical description of the case and all clinical maternal, fetal, and placental findings, and results of PCR bacteriological investigation and minimally invasive tissue sampling histology, from all eligible preterm neonates to determine the primary and contributing maternal, placental, and neonatal causes of death.
Findings: Between July 1, 2018, and March 26, 2020, of the 3470 preterm neonates enrolled, 804 (23%) died by 28 days after birth, and, of those, 615 were eligible and had their cases reviewed by the panel. Primary maternal causes of neonatal death were hypertensive disease (204 [33%] of 615 cases), followed by maternal complication of pregnancy (76 [12%]) and preterm labour (76 [11%]), whereas the primary placental causes were maternal and fetal vascular malperfusion (172 [28%] of 615) and chorioamnionitis, funisitis, or both (149 [26%]). The primary neonatal cause of death was intrauterine hypoxia (212 [34%] of 615) followed by congenital infections (126 [20%]), neonatal infections (122 [20%]), and respiratory distress syndrome (126 [20%]).
Interpretation: In south Asia, intrauterine hypoxia and congenital infections were the major causes of neonatal death among preterm babies. Maternal hypertensive disorders and placental disorders, especially maternal and fetal vascular malperfusion and placental abruption, substantially contributed to these deaths.
Funding: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests We declare no competing interests.
Comment in
-
Preterm births and deaths: from counting to classification.Lancet Glob Health. 2022 Nov;10(11):e1537-e1538. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00422-3. Lancet Glob Health. 2022. PMID: 36240810 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hug L, Sharrow D, You D, UN Inter-Agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation Levels and trends in child mortality: report 2017. 2017. https://reliefweb.int/attachments/c6e478e4-9107-38c2-833f-ff709cc80851/C...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical