Efficacy of Moraceae with chlorhexidine mouthwash on the microbial flora of critically ill intubated patients: a randomized controlled pilot study
- PMID: 36241889
- PMCID: PMC9568567
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-21556-y
Efficacy of Moraceae with chlorhexidine mouthwash on the microbial flora of critically ill intubated patients: a randomized controlled pilot study
Abstract
Critically ill intubated patients are routinely provided with chlorhexidine (CHX) for their mouth washing, but CHX mouthwash induces several complications. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Moraceae with CHX mouthwash in the reduction of oral bacterial count in critically ill patients and to compare it with CHX-alone mouthwash. This double-blind, randomized, controlled trial included critically ill patients receiving mechanical ventilation. The patients were randomly divided into two groups based on the Modified Beck oral assessment score. The primary endpoint was a reduction in oral bacterial counts after mouth washing on day 1 and day 4. Thirty patients were included in this study; 15 patients received Moraceae with CHX mouthwash and 15 patients received CHX-alone mouthwash. The oral bacterial counts in the Moraceae with CHX group did not differ from the CHX group after mouth washing on day 1 and day 4 of admission. The patients in the CHX group experienced more intolerable taste than those in the Moraceae group (60% vs. 13.3%, P = 0.008). Moraceae with CHX mouthwash had the same effectiveness as CHX alone on bacterial flora but exhibited less intolerable side effects than CHX alone.Trial registration: TCTR20190530003; 30/05/2019.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
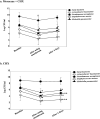
Similar articles
-
Oral mucosal mouthwash with chlorhexidine does not reduce the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically ill children: A randomised controlled trial.Aust Crit Care. 2022 Jul;35(4):336-344. doi: 10.1016/j.aucc.2021.06.011. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Aust Crit Care. 2022. PMID: 34376358 Clinical Trial.
-
Chlorhexidine with an anti discoloration system after periodontal flap surgery: a cross-over, randomized, triple-blind clinical trial.J Clin Periodontol. 2008 Jul;35(7):614-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01238.x. Epub 2008 Apr 16. J Clin Periodontol. 2008. PMID: 18422695 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of two mouthwashes on 3-day supragingival plaque regrowth: a randomized crossover clinical trial.Int J Dent Hyg. 2017 Feb;15(1):73-80. doi: 10.1111/idh.12185. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Int J Dent Hyg. 2017. PMID: 26522915 Clinical Trial.
-
Chlorhexidine mouthwash and sodium lauryl sulphate dentifrice: do they mix effectively or interfere?Int J Dent Hyg. 2016 Feb;14(1):42-52. doi: 10.1111/idh.12125. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Int J Dent Hyg. 2016. PMID: 25880828 Review.
-
Effects of chlorhexidine mouthwash on the oral microbiome.J Dent. 2021 Oct;113:103768. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2021.103768. Epub 2021 Aug 18. J Dent. 2021. PMID: 34418463 Review.
Cited by
-
Oral hygiene care for critically ill patients to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 24;12(12):CD008367. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008367.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33368159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torres A, et al. International ERS/ESICM/ESCMID/ALAT guidelines for the management of hospital-acquired pneumonia and ventilator-associated pneumonia: Guidelines for the management of hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP)/ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) of the European respiratory society (ERS), European Society of Intensive care medicine (ESICM), European society of clinical microbiology and infectious diseases (ESCMID) and Asociación latinoamericana del Tórax (ALAT). Eur. Respir. J. 2017 doi: 10.1183/13993003.00582-2017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baradari AG, Khezri HD, Arabi S. Comparison of antibacterial effects of oral rinses chlorhexidine and herbal mouth wash in patients admitted to intensive care unit. Bratisl. Lek. Listy. 2012;113:556–560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

