PCSK9 promotes the progression and metastasis of colon cancer cells through regulation of EMT and PI3K/AKT signaling in tumor cells and phenotypic polarization of macrophages
- PMID: 36242053
- PMCID: PMC9563506
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-022-02477-0
PCSK9 promotes the progression and metastasis of colon cancer cells through regulation of EMT and PI3K/AKT signaling in tumor cells and phenotypic polarization of macrophages
Abstract
Background: Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) is the ninth member of the proprotein convertase family that regulates lipoprotein homeostasis and altered PCSK9 expression was reportedly associated with tumor development and progression. This study assessed PCSK9 expression and functions in human colon cancer and then explored the underlying molecular events.
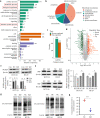
Methods: Colon cancer tissues were utilized for analysis of PCSK9 expression for association with clinicopathological factors from patients by immunohistochemistry assay. Manipulation of PCSK9 expression was assessed in vitro and in vivo for colon cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion using cell viability CCK-8, Transwell tumor cell migration and invasion, and wound-healing assays. Next, proteomic analysis, Western blot, qRT-PCR and Flow cytometry were conducted to assess downstream targets and tumor cell-derived PCSK9 action on macrophage polarization.
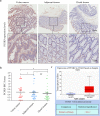
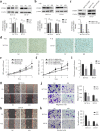
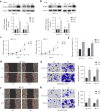
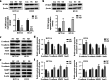
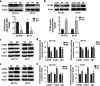
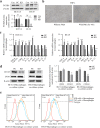
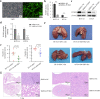
Results: PCSK9 expression was upregulated in colon cancer tissues versus the normal tissues, and associated with advanced tumor pathological grade. Knockdown of PCSK9 expression reduced colon cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and suppressed tumor metastasis in vivo. PCSK9 directly or indirectly upregulated Snail 1 and in turn to downregulate E-cadherin expression, but upregulate N-cadherin and MMP9 levels and thereafter, to induce colon cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process and activated PI3K/AKT signaling. However, PCSK9 overexpression showed the inverse effects on colon cancer cells. Knockdown of PCSK9 expression inhibited M2 macrophage polarization, but also promoted M1 macrophage polarization by reduction of lactate, protein lactylation and macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) levels.
Conclusion: PCSK9 played an important role in the progression and metastasis of colon cancer by regulation of tumor cell EMT and PI3K/AKT signaling and in the phenotypic polarization of macrophages by mediating MIF and lactate levels. Targeting PCSK9 expression or activity could be used to effectively control colon cancer.
Keywords: AKT; Colon cancer; EMT; Macrophage polarization; PCSK9; PI3K.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LncRNA DLEU2 silencing impedes the migration, invasion and EMT in gastric cancer cell by suppressing PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022 Oct;44(5):719-731. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2022.2078727. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022. PMID: 35736813
-
Calycosin inhibits triple-negative breast cancer progression through down-regulation of the novel estrogen receptor-α splice variant ER-α30-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2023 Sep;118:154924. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154924. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37393829
-
Microrchidia family CW‑type zinc finger 2 promotes the proliferation, invasion, migration and epithelial‑mesenchymal transition of glioma by regulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling via binding to N‑myc downstream regulated gene 1 promoter.Int J Mol Med. 2022 Feb;49(2):16. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.5071. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34913078 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted role of PCSK9 in cancer pathogenesis, tumor immunity, and immunotherapy.Med Oncol. 2024 Jul 15;41(8):202. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02435-0. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39008137 Review.
-
An Update on S100A16 in Human Cancer.Biomolecules. 2023 Jul 3;13(7):1070. doi: 10.3390/biom13071070. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37509106 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Mitochondrial Cholesterol Efflux via TCF21/ABCA10 Pathway to Enhance Cisplatin Efficacy in Ovarian Cancer.Biochem Genet. 2024 Oct 22. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-10939-7. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 39438390
-
Comprehensive analysis of clinical prognosis and biological significance of CNIH4 in cervical cancer.Cancer Med. 2023 Dec;12(24):22381-22394. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6734. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 38087815 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship and clinical significance of lactylation modification in digestive system tumors.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Jul 15;24(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03429-8. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39010066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Tumor Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Macrophage Crosstalk in Cancer Progression.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2023 Apr;21(2):117-127. doi: 10.1007/s11914-023-00780-z. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2023. PMID: 36848026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chimeric Peptide Engineered Nanomedicine for Synergistic Suppression of Tumor Growth and Therapy-Induced Hyperlipidemia by mTOR and PCSK9 Inhibition.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 23;15(10):2377. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15102377. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37896137 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Colombet M, Mery L, Pieros M, Znaor A, Soerjomataram I, Bray F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2018. https://gco.iarc.fr/today. Accessed 20 Feb 2019.
-
- Hu XH, Niu WB, Zhang JF, Li BK, Yu B, Zhang ZY, Zhou CX, Zhang XN, Gao Y, Wang GY. Treatment strategies for colorectal cancer patients in tumor hospitals under the background of corona virus disease. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;23(3):201–208. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn.441530-20200217-00058. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

