A haplodiploid mite adjusts fecundity and sex ratio in response to density changes during the reproductive period
- PMID: 36242724
- PMCID: PMC9732065
- DOI: 10.1007/s10493-022-00749-0
A haplodiploid mite adjusts fecundity and sex ratio in response to density changes during the reproductive period
Abstract
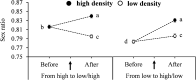
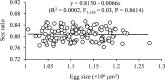
Population density is one of the main socio-environmental factors that have critical impacts on reproduction of animals. Consequently, they need to adjust their reproductive strategies in response to changes of local population density. In this study we used a haplodiploid spider mite, Tetranychus ludeni Zacher (Acari: Tetranychidae), to test how population density dynamics during the reproductive period altered female reproductive performance. We demonstrate that females produced fewer eggs with a significantly higher female-biased sex ratio in dense populations. Reducing fecundity and increasing daughter production in a dense environment could be an advantageous strategy to minimise the intensity of local food competition. However, females also reduced their fecundity after arrival in a new site of larger area from a dense population, which may be associated with higher web production costs because females need to produce more webs to cover the larger area. There was no trade-off between egg number and size, and egg size had little impact on reproductive fitness. Therefore, T. ludeni females could adapt to the shift of population density during their reproductive period by manipulating the fecundity and offspring sex ratio but not the egg size.
Keywords: Fecundity; Resource competition; Sex ratio; Social environment; Spider mite.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ashley JL (2003) Toxicity of selected acaricides on Tetranychus urticae Koch (Tetranychidae: Acari) and Orius insidiosus Say (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) life stages and predation studies with Orius insidiosus. MSc thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, p 60
-
- Azandémè-Hounmalon GY, Fellous S, Kreiter S, Fiaboe KKM, Subramanian S, Kungu M, Martin T. Dispersal behavior of Tetranychus evansi and T. urticae on tomato at several spatial scales and densities: implications for integrated pest management. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(4):e95071. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095071. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bengtsson J (2008) Aggregation in non-social insects: an evolutionary analysis. https://www.pub.epsilon.slu.se/3437/1/Aggregation_17_v2.pdf. Accessed 05 Feb 2022
-
- Bowden RM, Harms HK, Paitz RT, Janzen FJ. Does optimal egg size vary with demographic stage because of a physiological constraint? Funct Ecol. 2004;18:522–529. doi: 10.1111/j.0269-8463.2004.00861.x. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

