DNA rare copy number alterations in Reinke's Edema
- PMID: 36243603
- PMCID: PMC10071534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2022.09.002
DNA rare copy number alterations in Reinke's Edema
Abstract
Introduction: Reinke's Edema (RE) is a laryngeal lesion related to excessive tobacco smoking, voice overuse, and laryngopharyngeal reflux. Although the risk of malignancy has been considered low in literature, RE is classified among precancerous lesions.
Objectives: We investigated DNA Copy Number Alterations (CNAs) in specimens of RE and its potential association with malignant progression.
Methods: We used array-based comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH, Agilent 4 × 180 K platform) to study eight RE cases. All patients were heavy tobacco users for at least 30 years, and none of them progressed to cancer in the follow-up (>8 years). Two RE presented mild dysplasia, one moderate dysplasia, and no histological alterations were found in the remaining five cases. CNAs were compared with the Database of Genomic Variants (DGV) and genes mapped on altered regions had their functions annotated.
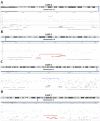
Results: Six of eight patients showed different rare copy number alterations on chromosomes 2q37.3, 4q13.1, 4q13.3, 7q11.22, 10p14, and 13q34. A gain of the whole chromosome 8 were detected in one case. Of interest, four of eight RE cases showed copy number imbalances involving genes previously described in several tumor types (RASA3, COL6A3, LINC00707, LINP1, SMR3A, and SMR3B).
Conclusion: The genomic imbalances herein found in RE have the potential to contribute to the phenotype but with limited or no risk of cancer. A long-term follow-up in a large series of patients could clarify the mechanisms involved in the malignant progression of RE.
Keywords: DNA copy number variations; Genomic medicine; Laryngeal edema; Microarray analysis; Preneoplastic condition.
Copyright © 2022 Associação Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia Cérvico-Facial. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Hah J.H., Sim S., An S.Y., Sung M.W., Choi H.G. Evaluation of the prevalence of and factors associated with laryngeal diseases among the general population. Laryngoscope. 2015;125:2536–2542. - PubMed
-
- Martins R.H.G., do Amaral H.A., Tavares E.L.M., Martins M.G., Gonçalves T.M., Dias N.H. Voice disorders: etiology and diagnosis. J Voice. 2016;30 761.e1–9. - PubMed
-
- Móz L.E., Domingues M.A., Castilho E.C., Branco A., Martins R.H.G. Comparative study of the behavior of p53 immunoexpression in smoking associated lesions: Reinke’s edema and laryngeal carcinoma. Inhal Toxicol. 2013;25:17–20. - PubMed
-
- Marcotullio D., Magliulo G., Pezone T. Reinke’s edema and risk factors: clinical and histopathologic aspects. Am J Otolaryngol. 2002;23:81–84. - PubMed
-
- Pastuszek P., Krecicki T., Zalesska-krecicka M., Jelen M., Rak J., Krajewska B. Histological and electron microscopic investigation of Reinke’s edema. Pol J Pathol. 2003;54:61–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous