Using a mixed method to identify communication skills training priorities for Chinese general practitioners in diabetes care
- PMID: 36243695
- PMCID: PMC9569069
- DOI: 10.1186/s12875-022-01868-8
Using a mixed method to identify communication skills training priorities for Chinese general practitioners in diabetes care
Abstract
Background: In China diabetes care is gradually shifting from secondary to primary care with great infrastructure investment and GP training. However, most GPs in China lack communication skills training, which is a huge obstacle in communication with their patients in primary care. In this study we seek to identify training priorities that is evidence-based, appropriate for the context of primary care in China, and that meet the real needs of both GPs and people with diabetes.
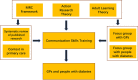
Methods: A mixed method approach was used. A conceptual framework was designed based on the MRC framework, action research and adult learning theories. Through a systematic review of the literature and qualitative research with GPs and patients with diabetes, a list of communication skills training components was developed by the research team. A modified nominal group technique (NGT) with GPs was used to evaluate these contents. Purposive sampling was used to recruit a variation of participants (age, work area, practice years and education background) from general practices in Guangzhou city, China. Eight structured nominal groups were facilitated to elicit the views of group members, and participants rated the 9-point Likert scale of importance and feasibility of the training items independently, before and after focus groups. The ranking of each item was calculated, based on the mean Likert score ratings from all participants. Video recordings of four NGT group discussions were thematically analysed using the Framework Method to explore reasons for any differences in rating items.
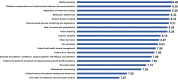
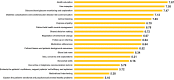
Results: 29 males and 29 female GPs from 28 general practices participated in NGT group discussions, with a mean age of 38.5 years and mean 12.3 years of practice experience. Based on the mean scores of importance and feasibility rating scores, the top 3 ranked priorities for communication training were 'health education' (importance 8.39, feasibility 7.67), 'discussing and explaining blood glucose monitoring' (8.31, 7.46), and 'diabetes complications and cardiovascular disease risk communication' (8.36, 7.12). Five main themes were identified from focus group discussions through qualitative analysis: 'impact on diabetes patients', 'GP attitudes towards communication skills', 'patient-related factors influencing the application of communication skills by GPs, 'local contextual factors', and 'training implementation'.
Conclusions: Priorities for communication skills training for Chinese GPs in diabetes care were identified. These are set in the context of GPs' current experience of communication with patients in China who have diabetes, which is often unsatisfactory. This study describes the baseline from which better primary care for diabetes in China needs to be developed. Based on suggestions from GPs themselves, it identifies an agenda for improvement in communication as a key component of diabetes care in China.
Keywords: Communication; Diabetes care; General practitioners; Training.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any competing interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA, Ogurtsova K et al: Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2019, 157:107843. - PubMed
-
- China NHCotPsRo: China health statistical yearbook 2019. Beijing: Peking union medical college publishing house; 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical