Association of lipid profile and reported edentulism in the elder population: data from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
- PMID: 36243707
- PMCID: PMC9571461
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-022-02492-9
Association of lipid profile and reported edentulism in the elder population: data from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
Abstract
Objectives: Relationship between lipid profile and periodontitis has been reported. However, the association between lipid parameters and edentulism is unclear. This study aimed to investigate the association between lipid profile and reported edentulism in the elder population using a national cohort.
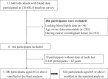
Methods: A total of 3 100 participants aged 65 or above were enrolled in 2011 from China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study, which was a national population-based survey. We used adjusted logistics models to investigate the relationship between lipid profile and reported edentulism before and after propensity score matching.
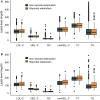
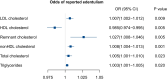
Results: The mean (SD) age was 71.96 (5.63) years, and 1 581 (51.0%) were men. There were 254 (8.2%) individuals reporting edentulism, and the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) was significantly higher in the reported edentulism group, compared with the non-edentulism (122.48 vs. 116.91 mg/dl, P = 0.015). In the multivariable model, LDL-C was significantly associated with a higher odds of reported edentulism (adjusted OR [95% CI], 1.004 [1.001-1.008]). In the matched population, LDL-C, non high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, remnant cholesterol, total cholesterol and triglycerides were positively associated with reported edentulism, while HDL-C was negatively associated.
Conclusions: Lipid profiles are probably associated with edentulism, indicating the interaction between oral health and metabolic status in the elder population.
Keywords: Elder population; LDL cholesterol; Lipid profile; Reported edentulism.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A non-linear connection between the total cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and stroke risk: a retrospective cohort study from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Mar 16;29(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01769-9. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38491452 Free PMC article.
-
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and all-cause mortality: findings from the China health and retirement longitudinal study.BMJ Open. 2020 Aug 16;10(8):e036976. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-036976. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32801200 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal lipid profile in pregnancy and embryonic size: a population-based prospective cohort study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022 Apr 18;22(1):333. doi: 10.1186/s12884-022-04647-6. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022. PMID: 35436866 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Lipid Levels With the Prevalence of Hypertension in Chinese Women: A Cross-Sectional Study Based on 32 Health Check Centers.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 7;13:904237. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.904237. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35873005 Free PMC article.
-
LDL-cholesterol to HDL-cholesterol ratio discordance with lipid parameters and carotid intima-media thickness: a cohort study in China.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Jun 18;19(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01324-5. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32552893 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The impact of physical activity on the prevalence of edentulism: an analysis of the relationships between active lifestyle and dental health.BMC Public Health. 2024 Oct 8;24(1):2743. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20242-0. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39379907 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical