Revisiting the anticancer properties of phosphane(9-ribosylpurine-6-thiolato)gold(I) complexes and their 9H-purine precursors
- PMID: 36244017
- PMCID: PMC9653339
- DOI: 10.1007/s00775-022-01968-x
Revisiting the anticancer properties of phosphane(9-ribosylpurine-6-thiolato)gold(I) complexes and their 9H-purine precursors
Abstract
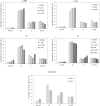
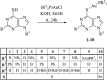
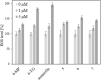
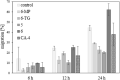
New mono- and di-nuclear thio-purine and thio-purine nucleoside gold(I) complexes were synthesized, characterized, and evaluated in vitro for biological activities in comparison to related known purine complexes. By combining known anti-tumoral thio-purines with R3PAu moieties as present in auranofin, complexes with enhanced effects and selectivities were obtained, which not only act as cytostatics, but also disrupt tumor-specific processes. Their IC50 values in cytotoxicity test with tumor cell lines ranged from three-digit nanomolar to single-digit micromolar, revealing a tentative structure-activity relationship (SAR). Both the residues R2 of the phosphane ligand and R1 at C2 of the pyrimidine ring had a significant impact on the cytotoxicity. In most cases, the introduction of a ribo-furanosyl group at N9 of the purine led to a distinctly more cytotoxic complex. Most complexes were more active against multi-drug-resistant tumor cells or such lacking functional p53 when compared to the respective untreated wild type cell lines. Some nucleoside complexes displayed an interesting dose-dependent dual mode of action regarding cell cycle arrest and DNA repair mechanism. Some phosphane(purine-6-thiolato)gold (I) complexes had a stronger inhibitory effect on the thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) and on the reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in cancer cells than is typical of other gold complexes. They also led to DNA fragmentation and showed anti-angiogenic effects. Their stability under test conditions was demonstrated by 77Se NMR monitoring of an exemplary selenopurine complex.
Keywords: Anticancer compounds; Auranofin; Gold(I) complexes; Nucleosides; Thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) inhibitors; Triorganophosphanes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ott I, Gust R. Non platinum metal complexes as anti-cancer drugs. Arch Pharm. 2007;340:117–126. - PubMed
-
- Bernhard GC. Auranofin therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. J Lab Clin Med. 1982;100:167–177. - PubMed
-
- Raninga PV, Lee AC, Sinha D, Shik Y-Y, Mittal D, Makhale A, et al. Therapeutic cooperation between auranofin, a thioredoxin reductase inhibitor and anti-PD-L1 antibody for treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2020;146:123–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

