Higher sensitivity and accuracy of synovial next-generation sequencing in comparison to culture in diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36244018
- PMCID: PMC10435641
- DOI: 10.1007/s00167-022-07196-9
Higher sensitivity and accuracy of synovial next-generation sequencing in comparison to culture in diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this meta-analysis was to compare the diagnostic parameters of synovial next-generation sequencing (NGS) and cultures in diagnosing periprosthetic joint infections (PJI).
Methods: PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane, and Google Scholar were searched from inception until 8 Jan 2022 for literature investigating the role of NGS in comparison to culture in the diagnosis of PJI. The studies were included if they investigated the diagnostic value of culture and NGS in diagnosing PJIs against the Musculoskeletal Infection Society (MSIS) criteria. Diagnostic parameters, such as sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, positive-likelihood ratio, negative-likelihood ratio, accuracy, and area under the curve (AUC), were calculated for the included studies to evaluate the performance of NGS in comparison to culture in PJI diagnosis.
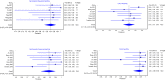
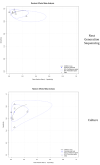
Results: The total number of the included patients was 341 from seven articles. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic odds ratio of NGS were 94% (95% CI 91-97%), 89% (95% CI 82-95%), and 138.5 (95% CI 49.1-390.5), respectively. NGS has positive- and negative-likelihood ratios of 7.9 (95% CI 3.99-15.6) and 0.1 (95% CI 0.0-0.1), respectively. On the other hand, the pooled sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic odds ratio of culture were 70% (95% CI 61-79%), 94% (95% CI 88-98%), and 28.0 (95% CI 12.6-62.2), respectively. The SROC curve for NGS showed that the accuracy (AUC) was 91.9%, and that the positive and negative predictive values were 8.6 (95% CI 5.0-19.5) and 0.1 (95% CI 0.0-0.1), respectively. While, culture SROC curve demonstrated that the accuracy (AUC) was 80.5% and the positive- and negative-likelihood ratio were 12.1 (95% CI 4.5-49.6) and 0.3 (95% CI 0.2-0.4).
Conclusions: NGS has a potential role in diagnosing hip and knee PJIs due to its high sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy. However, the sensitivity and specificity reported by the studies varied according to the time of synovial sampling (preoperative, postoperative, or mixed).
Keywords: Arthroplasty; Culture; Diagnosis; Next-generation sequencing; Periprosthetic joint infection.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article. All authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bukowska-Ośko I, Perlejewski K, Nakamura S, et al. Sensitivity of next-generation sequencing metagenomic analysis for detection of RNA and DNA viruses in cerebrospinal fluid: the confounding effect of background contamination. respiratory treatment and prevention. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016 doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_42. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

