Pax2a, Sp5a and Sp5l act downstream of Fgf and Wnt to coordinate sensory-neural patterning in the inner ear
- PMID: 36244503
- PMCID: PMC12306526
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2022.10.004
Pax2a, Sp5a and Sp5l act downstream of Fgf and Wnt to coordinate sensory-neural patterning in the inner ear
Abstract
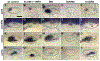
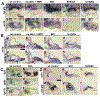
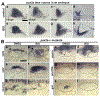
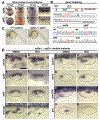
In zebrafish, sensory epithelia and neuroblasts of the inner ear form simultaneously in abutting medial and lateral domains, respectively, in the floor of the otic vesicle. Previous studies support regulatory roles for Fgf and Wnt, but how signaling is coordinated is poorly understood. We investigated this problem using pharmacological and transgenic methods to alter Fgf or Wnt signaling from early placodal stages to evaluate later changes in growth and patterning. Blocking Fgf at any stage reduces proliferation of otic tissue and terminates both sensory and neural specification. Wnt promotes proliferation in the otic vesicle but is not required for sensory or neural development. However, sustained overactivation of Wnt laterally expands sensory epithelia and blocks neurogenesis. pax2a, sp5a and sp5l are coregulated by Fgf and Wnt and show overlapping expression in the otic placode and vesicle. Gain- and loss-of-function studies show that these genes are together required for Wnt's suppression of neurogenesis, as well as some aspects of sensory development. Thus, pax2a, sp5a and sp5l are critical for mediating Fgf and Wnt signaling to promote spatially localized sensory and neural development.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; Hair cells; Statoacoustic ganglion; atoh1a; neurog1.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fgf, Hh, and pax2a differentially regulate expression of pax5 and pou3f3b in vestibular and auditory maculae in the zebrafish otic vesicle.Dev Dyn. 2023 Oct;252(10):1269-1279. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.599. Epub 2023 May 12. Dev Dyn. 2023. PMID: 37171017 Free PMC article.
-
sox2 and sox3 Play unique roles in development of hair cells and neurons in the zebrafish inner ear.Dev Biol. 2018 Mar 1;435(1):73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.01.010. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29355523 Free PMC article.
-
Pax2a, Pax5 and Cdh1-β-catenin, but not Wnt, protect sensory hair cells from destabilizing effects of fgf signaling on cell adhesion.Dev Biol. 2025 Jan;517:157-167. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2024.09.009. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 39332789
-
Comparative assessment of Fgf's diverse roles in inner ear development: A zebrafish perspective.Dev Dyn. 2021 Nov;250(11):1524-1551. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.343. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Dev Dyn. 2021. PMID: 33830554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Search of a Target Gene for a Desirable Phenotype in Aquaculture: Genome Editing of Cyprinidae and Salmonidae Species.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jun 1;15(6):726. doi: 10.3390/genes15060726. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Introgression dynamics of sex-linked chromosomal inversions shape the Malawi cichlid radiation.Science. 2025 Jun 12;388(6752):eadr9961. doi: 10.1126/science.adr9961. Epub 2025 Jun 12. Science. 2025. PMID: 40504893 Free PMC article.
-
Fgf, Hh, and pax2a differentially regulate expression of pax5 and pou3f3b in vestibular and auditory maculae in the zebrafish otic vesicle.Dev Dyn. 2023 Oct;252(10):1269-1279. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.599. Epub 2023 May 12. Dev Dyn. 2023. PMID: 37171017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abelló G, Khatri S, Radosevic M, Scotting PJ, Giráldez F and Alsina B (2010). Independent regulation of Soc3 and Lmx1b by FGF and BMP signaling influences the neurogenic and non-neurogenic domains of the chick otic placode. Dev. Biol 339. 166–178. - PubMed
-
- Alsina B, Abelló G, Ulboa E, Henrique D, Pujades C and Giraldez F (2004). FGF signaling is required for determination of otic neuroblasts in the chick embryo. Dev. Biol 267, 119–134. - PubMed
-
- Brand M, Heisenberg C-P, Jiang Y-J, Beuchle D, Lun K, Furutani-Seiki M, Granato M, Haffter P, Hammerschmidt M, Kane D, Kelsh R, Mullins M, Odenthal J, van Eeden FJM and Nüsslein-Valhard C (1996). Mutations in zebrafish affecting the formation of the boundary between midbrain and hindbrain. Development 123, 179–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

