Comparison of behavioral and brain indices of fear renewal during a standard vs. novel immersive reality Pavlovian fear extinction paradigm in healthy adults
- PMID: 36244544
- PMCID: PMC10277015
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2022.114154
Comparison of behavioral and brain indices of fear renewal during a standard vs. novel immersive reality Pavlovian fear extinction paradigm in healthy adults
Abstract
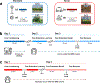
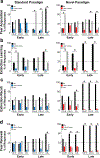
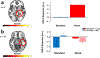
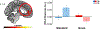
Pavlovian conditioning paradigms model the learned fear associations inherent in posttraumatic stress disorder, including the renewal of inappropriate fear responses following extinction learning. However, very few studies in humans investigate the underlying neural mechanisms involved in fear renewal despite its clinical importance. To address this issue, our lab designed a novel, immersive-reality Pavlovian fear acquisition, extinction, recall, and renewal paradigm. We utilized an ecological threat - a snake striking towards the participant - as the unconditioned stimulus (US). Context and background were dynamic and included both visual and auditory cues that are relevant to everyday life. Using functional magnetic resonance imaging and behavioral measures (US expectancy ratings), we examined the validity of this Novel paradigm in healthy adults (n = 49) and compared it to a Standard, well-validated 2D paradigm (n = 28). The Novel paradigm, compared to the Standard, was associated with greater hippocampal activation throughout the task. Participants who underwent the Standard paradigm, compared to the Novel, also displayed insula activation; however, this was not specific to stimulus or time. During fear renewal, the Novel paradigm was associated with dorsal anterior cingulate cortex activation to CS+ (> CS-). Overall, we found that our Novel, immersive-reality paradigm, which features an ecologically relevant US, elicited greater corticolimbic activation. These results suggest that immersive Pavlovian fear conditioning paradigms paired with innately fearful stimuli may improve translatability of preclinical paradigms to clinical interventions for fear-based disorders.
Keywords: Amygdala; FMRI; Fear renewal; Hippocampus; Prefrontal cortex; Virtual reality.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

